中文词条原文链接(无法从中国内地访问):请点击这里访问
英文词条原文链接(无法从中国内地访问):请点击这里访问
本文基于英文词条的线索,并补充部分来自中文词条的内容(在二者冲突时,以更晚更新者为准)。辽观搬运时进行了必要的合规化处理,以使其能够在中国内地上传。部分文字采用汉语拼音方式代替,音节后的数字表示汉语拼音规则中的声调。
关于辽观的维基百科搬运计划,及根据名称精确检索已搬运的词条,请点击这里访问辽观网站。维基百科(Wikipedia)是美国维基媒体基金会的互联网百科项目,其内容可能受到立场、信息来源等因素影响,请客观看待。正文内容不代表译者观点。
辽观提供的翻译仅供参考。文中可能包含无法从中国内地访问的链接。
辽观所搬运的词条文本与维基百科一道同样遵循CC BY-SA 4.0协议(辽观搬运的中英文对照版本),在符合协议要求的情况下您可以免费使用其内容(包括商用)。图片和视频可能遵循不同的共享协议。请点击这里访问
目录
- 0. 概述
- 1. 名称由来 | Etymology
- 1. 历史 | History
- 2. 地理 | Geography
- 3. 政治
- 4. 人口 | Demographics
- 5. 交通 | Transport
- 6. 经济 | Economy
- 7. 社会与文化 | Society and culture
- 8. 外部交往
- 9. 知名人物 | Notable residents
- 参见、参考文献、外部链接
0. 概述
辽观注:此标题是我们在搬运、整合过程中添加的。
0.1 文字说明
辽观注:此标题是我们在搬运、整合过程中添加的。
昆明市,简称昆,别称“春城”,是中华人民共和国云南省省会,面向南亚东南亚的区域性中心城市,国家历史文化名城,国际性综合交通枢纽城市[1],也是云南的政治、经济、文化、科技中心和交通枢纽。昆明素以“春城”著称,因其夏无酷暑、冬无严寒、气候宜人,具有典型的温带气候特点。昆明是国家历史文化名城,拥有世界自然遗产云南石林,国家级风景名胜区滇池,轿子山国家级自然保护区,西山国家森林公园,以及众多的全国重点文物保护单位。面积21,013平方公里,2020年总人口846.01万,市人民政府驻呈贡区。
Kunming[a] is the capital and largest city of the province of Yunnan in China.[4] The political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province, Kunming is also the seat of the provincial government. During World War II, Kunming was a Chinese military center and the location of the headquarters for the US Army Forces China-Burma-India.[5] Wujiaba Airport served as the home of the First American Volunteer Group (AVG) of the Republic of China Air Force, nicknamed the Flying Tigers.[6] Kunming was also a transport terminus for the Burma Road.
【参考译文】昆明[a]是中国云南省的省会及最大城市。[4]作为该省的政治、经济、通讯和文化中心,昆明也是省政府所在地。在第二次世界大战期间,昆明是中国的军事中心,并且是美军驻中国-缅甸-印度司令部所在地。[5]巫家坝机场曾是中华民国空军美国志愿援华航空队(AVG,又称飞虎队)的驻地。[6]昆明还是滇缅公路的运输终点站。
【英文词条原注a】/kʊnˈmɪŋ/;[3] Chinese: 昆明; pinyin: Kūnmíngw
Kunming is at an altitude of 1,900 metres (6,234 feet) above sea level and a latitude just north of the Tropic of Cancer, and is situated in the middle of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. Kunming is the fourth most populous city in Western China, after Chongqing, Chengdu, and Xi’an, and the third most populous city in Southwestern China after Chongqing and Chengdu. As of the 2020 census, Kunming had a total population of 8,460,088 inhabitants, of whom 5,604,310 lived in its built-up (or metro) area made of all urban districts except Jinning. It is at the northern edge of Dian Lake, surrounded by temples and lakes and karst topography.[7]
【参考译文】昆明海拔1900米(6234英尺),位于北回归线稍北的位置,坐落于云贵高原中部。昆明是中国西部第四大城市,仅次于重庆、成都和西安,同时也是中国西南部第三大城市,仅次于重庆和成都。根据2020年人口普查,昆明总人口为8,460,088人,其中5,604,310人居住在由所有城区(金宁区除外)组成的建成区(或市区)。它位于滇池的北岸,四周环绕着寺庙、湖泊和喀斯特地貌。[7]
Kunming consists of an old, previously walled city, a modern commercial district, residential zones, and university areas. The city is also one of the major centers for scientific research and education in Southwestern China. As of 2024, it was listed among the top 100 cities in the world by scientific research output.[8] The city has an astronomical observatory, and its institutions of higher learning include Yunnan University, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Normal University, Yunnan Agricultural University and Southwest Forestry University. Kunming is also home to the Golden Temple, China’s largest bronze temple dating from the Ming dynasty.
【参考译文】昆明由一座古老且之前筑有城墙的城区、一个现代化的商业区、居住区以及大学区组成。这座城市也是中国西南部主要的科研和教育中心之一。截至2024年,昆明凭借科研产出位列世界城市前100名。[8]昆明拥有一座天文台,其高等教育机构包括云南大学、昆明理工大学、云南财经大学、昆明医科大学、云南师范大学、云南农业大学和西南林业大学。昆明还是中国最大的明代青铜寺庙——金殿的所在地。
Kunming is a major economic center in Western China. The city’s economic importance derives from its geographical position, as it shares a border with various Southeast Asian countries, serving them as a transportation hub in Southwest China, linking by rail to Vietnam and Laos, and by road to Myanmar and Thailand. This positioning also makes the city an important commercial center of trade in the region. The city also acts as a gateway to Southeast Asia and South Asia, the Kunming Changshui International Airport is one of the top 40-busiest airports in the world.[9][10] As of 2024, the city is also home to six consulates from ASEAN countries.[11]
【参考译文】昆明是中国西部的一个重要经济中心。该城市的经济重要性源自其地理位置,它与多个东南亚国家接壤,是中国西南地区的一个交通枢纽,通过铁路与越南和老挝相连,通过公路与缅甸和泰国相通。这一地理位置也使昆明成为该地区一个重要的商业贸易中心。昆明还是通往东南亚和南亚的门户,昆明长水国际机场是全球最繁忙的40大机场之一。[9][10]截至2024年,该市还设有来自东盟国家的六个领事馆。[11]
The headquarters of many of Yunnan’s biggest corporations are based in the city, such as Hongta Group, Yunnan Copper Group, Hongyun Group, Yunnan Power Grid Co, and Fudian Bank.[12][13] Kunming also houses some manufacturing, chiefly the processing of copper, as well as various chemicals, machinery, textiles, paper and cement. Kunming has a nearly 2,400-year history, but its modern prosperity dates only to 1910, when the railway from Hanoi was built. The city has continued to develop rapidly under China’s modernization efforts. Kunming was designated a special tourism center and, as such, has experienced a proliferation of high-rises and luxury hotels.
【参考译文】许多云南大型企业的总部均设在昆明,如红塔集团、云南铜业集团、红云集团、云南电网公司和富滇银行。[12][13]昆明还拥有一些制造业,主要是铜加工以及各类化工、机械、纺织、造纸和水泥产业。昆明有近2400年的历史,但其现代繁荣期始于1910年河内铁路的修建。在中国现代化的进程中,昆明继续快速发展。昆明被指定为特殊旅游中心,因此高层建筑和豪华酒店不断涌现。
0.2 概况表格
辽观注:此标题是我们在搬运、整合过程中添加的。
| 地级市 | |
| 绰号:春城 | |
坐标: 25°02′30″N 102°42′18″E 25°02′30″N 102°42′18″E | |
| 国家 | 中华人民共和国 |
|---|---|
| 省 | 云南省 |
| 设立 | 1928年 |
| 政府驻地 | 呈贡区锦绣大街1号 |
| 下级行政区 | 7市辖区、1县级市、3县、3自治县 |
| 政府 | |
| • 市委书记 | 刘洪建 |
| • 人大常委会主任 | 杨正晓 |
| • 市长 | 刘佳晨 |
| • 政协主席 | 杨皕(女) |
| 面积 | |
| • 地级市 | 21,013 平方公里(8,113 平方英里) |
| • 市区 | 5,952 平方公里(2,298 平方英里) |
| 面积排名 | 全省第10位(占全云南省5.48%) |
| • 建成区(2022) | 456.15 平方公里(176.12 平方英里) |
| 最高海拔 | 4,247 米(13,934 英尺) |
| 人口(2022) | |
| • 常住 | 860万人 |
| • 排名 | 全省第1位(占全云南省17.92%) |
| • 密度 | 402.8人/平方公里(1,043人/平方英里) |
| • 市区(2020) | 534.09万人 |
| • 城镇(2022) | 674.05万人 |
| 语言 | |
| • 官方语言 | 普通话 |
| • 方言 | 西南官话(云南话、昆明话) |
| 时区 | 北京时间(UTC+8) |
| 邮政编码 | 650000 |
| 电话区号 | 871 |
| 车辆号牌 | 云A |
| 气候 | 亚热带季风气候 |
| • 年均温 | 15.7 ℃ |
| • 年降水 | 965.8毫米 |
| 行政区划代码 | 530100 |
| 旧称 | 云南府 |
| 国内生产总值(2020) | ¥6,733.79亿(全省第1位,占全云南省27.50%) 976.28亿美元(汇率) |
| • 人均 | ¥80,586(全省第2位) 11,684美元(汇率) |
| HDI(2016) | 0.729( 高 ) |
| 网站 | 昆明市人民政府门户网站 |
| 市象征 | |
| 花 | 茶花 |
| 树 | 玉兰树 |
| 本表经济数据参考《云南统计年鉴 2021》,人口数据参考《中国人口普查分县资料 2020》 人类发展指数数据参考《中国人类发展报告特别版》。 | |
1. 名称由来 | Etymology
“Kunming” evolved from the name of an ancient ethnic group called the Kunming Yi or Kunming Barbarian (昆明夷). They were a branch of the Di–Qiang people. The Kunming Yi lived in the neighbouring region of Erhai Lake during the Western Han dynasty. The Han dynasty incorporated the territory of the Dian Kingdom and set up a commandery called Yizhou in 109 BC; the Han dynasty also incorporated the Kunming Yi into Yizhou Commandery soon after. Therefore, Kunming Yi expanded east to the Lake Dian area later. “Kunming” has acted as a place name since the Three Kingdoms period, but the reference was not clear because this ethnicity occupied a large region. In the Yuan dynasty, the central government set up “Kunming County” in modern Kunming; the name “Kunming” has continued to this day.[14]
【参考译文】“昆明”一词源自古代一个名为昆明夷或昆明蛮的民族。他们是氐羌民族的一个分支。在西汉时期,昆明夷居住在洱海附近的区域。汉朝于公元前109年吞并滇国领土,并设立益州郡;不久后,汉朝也将昆明夷纳入益州郡管辖。因此,昆明夷后来向东扩张至滇池区域。“昆明”自三国时期起便作为一个地名使用,但由于该民族占据了大片区域,所以指代并不明确。在元朝时期,中央政府在现今昆明所在地设立“昆明县”,“昆明”这一名称一直沿用至今。[14]
A 2009 research paper proposes that the name “Kunming” of Kunming Yi is a cognate word of “Khmer” and “Khmu” that originally meant “people”.[15]
【参考译文】2009年的一篇研究论文提出,昆明夷的“昆明”一词与“高棉”(Khmer)和“克木”(Khmu)是同源词,原本意为“人”。[15]
关于“昆明”一词的起源有多种说法。大多数学者认为,“昆明”最初是中国西南地区一个古代民族的族称。“昆明”在中国古代文献中写作“昆”、“昆弥”或“昆淋”。早期并非城市名称,而是居住在中国西南地区即今日的云南西部、四川西南部的一个古代民族的族称。“昆明”一词的出现,可追溯到汉武帝时期。
而“昆明”作为地名出现则是在唐代。武德二年,于镇置昆明县,盖南接昆明之地,因此为名。此处昆明仍指昆明族而言,盖汉唐以前,昆明族大部定居云南西部地区。直到南诏、大理国时期,乌蛮、白蛮兴起,昆明族居住的地方,为乌蛮、白蛮据有,昆明族才东迁滇中,聚居于滇池周围。1254年,元灭大理,在鄯阐设 “昆明千户所”,“昆明”始作为地名出现,延续至今。“昆明”一词的含义,东晋常璩解释说:“夷人大种曰昆,小种曰叟。[2]”这句话可以解释为人口众多的昆明族。
1. 历史 | History
See also: History of Yunnan【参见:云南历史】
1.1 早期历史 | Early history
Kunming long profited from its position on the caravan route through to Southeast Asia, India and Tibet. Early townships on the southern edge of Lake Dian (outside the contemporary city perimeter) can be dated back to 279 BC, although they have been long lost to history. Early settlements in the area around Lake Dian date back to Neolithic times. The Dian Kingdom, whose original language likely belonged to the Tibeto-Burman languages, was also established near the area.[16]
【参考译文】昆明长期受益于其位于通往东南亚、印度和西藏的商队路线上的地理位置。滇池南岸(当代城市边界之外)的早期城镇可以追溯到公元前279年,尽管它们早已在历史的长河中消失。滇池周边地区的早期定居点可追溯到新石器时代。滇国也建立在这一地区附近,其原始语言可能属于藏缅语族。[16]
史书上对昆明地区最早的记载是公元前279年, 楚国大将庄跷远征到达滇池地区,由于秦国打败了楚国,无法回国,而被迫留在滇池以南地区,“变服从其俗”,建立了滇国。前109年(西汉元封二年),汉武帝加封常羌为滇王,赐给金印,称益州郡,下辖24县,辖区相当今云南大部,郡治滇池县(今昆明城南晋城、呈贡)。225年,诸葛亮南征也到达滇池地区,改为建宁郡,为爨氏所据。
Dian was subjugated by the Chinese Han dynasty under the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in 109 BC. The Han dynasty incorporated the territory of the Dian Kingdom into their Yizhou Commandery, but left the King of Dian as the local ruler.[17]
【参考译文】公元前109年,汉武帝统治时期,滇国被汉朝征服。汉朝将滇国的领土并入其益州郡,但保留了滇王作为当地的统治者。[17]
司马迁在《史记·西南夷列传》中写道:“西自同师(今怒江以东的保山市、昌宁、施甸等地[3])以东,北至叶榆,名为嶲、昆明、皆编发,随畜迁徙,毋常处,毋君长,地方可数千里。”
The Han dynasty (205 BC–AD 220), seeking control over the Southern Silk Road running to Burma and India, brought small parts of Yunnan into China’s orbit, but subsequent dynasties could do little to tame what was then a remote and wild borderland until the 13th century.[18][contradictory] During the Sui dynasty (581–618), two military expeditions were launched against the area, and it was renamed Kunzhou in Chinese sources.[19]
【参考译文】汉朝(公元前205年至公元220年)为了控制通往缅甸和印度的南方丝绸之路,将云南的部分地区纳入中国的势力范围,但随后的朝代直到13世纪才对当时偏远而荒蛮的边境地区进行有效的管辖。[18][有矛盾之处]在隋朝(581年至618年)期间,曾对该地区发动了两次军事远征,并在中文史料中将其改名为昆州。[19]
1.2 中古中国 | Medieval China
765年,南诏王阁罗凤决定向东拓展疆土,派其子凤伽异在今昆明市中心筑造拓东城,后改称鄯阐城(白语sit zaind 第二城之意),别称东都。是为昆明筑城之始。
Founded in 765, Kunming was known to the Chinese as Tuodong (拓東) city in the Kingdom of Nanzhao (737–902) during the 8th and 9th centuries.[19] Tuodong later became part of the successor Kingdom of Dali (937–1253).
【参考译文】昆明始建于765年,在8世纪和9世纪期间,于南诏国(737年至902年)统治之下,被中国人称为拓东城。[19]拓东后来成为大理国(937年至1253年)的一部分。
The possession of Tuodong changed hands when the city came under the control of the Yuan dynasty during its invasion of the southwest in 1252–1253. During the reign of provincial governor Ajall Shams al-Din Omar, a “Chinese Style” city named Zhongjing was founded where modern Kunming is today.
【参考译文】1252年至1253年间,在元朝入侵西南时,拓东城落入元朝之手,其所有权再次易主。在行省长官阿合马统治时期,于今日昆明之地建立了一座名为“中庆”的“汉式”城市。
1254年,蒙古大汗忽必烈派兵攻取鄯阐城。1276年(元至元十三年),蒙元设立云南行中书省,为全国13行省之一,首府为中庆(昆明),自此昆明取代大理成为云南的政治中心。
Shams al-Din ordered the construction of a Buddhist temple, a Confucian temple, and two mosques in the city.[20] The Confucian temple, doubling as a school, was the first of its kind in Yunnan, attracting students from minority groups across the province.[21] Coupled with his promotion of Confucian ceremonies and customs, Shams al-Din has been largely credited with the sinicization of the region.[22] The city grew as a trading center between the southwest and the rest of China. It is considered by scholars to have been the city of Yachi Fu (鸭池府) where people had used cowries as cash and ate their meat raw, as described by the 13th-century Venetian traveler Marco Polo.[23] The area was first dubbed Kunming during the decline of the Yuan Dynasty.
【参考译文】阿合马下令在城内建造一座佛寺、一座孔庙和两座清真寺。[20]孔庙同时作为学校使用,是云南的第一所此类学校,吸引了来自全省少数民族的学生。[21]阿合马大力推广儒家礼仪和习俗,因此人们普遍认为他对该地区的汉化做出了重大贡献。[22]昆明作为西南地区与中国其他地区之间的贸易中心不断发展壮大。学者们认为,马可·波罗这位13世纪的威尼斯旅行家所描述的,人们使用贝币作为现金且生食其肉的城市,就是鸭池府,即昆明。[23]在元朝衰落期间,该地区首次被称为昆明。
1.3 明清 | Ming and Qing dynasties
1381年(明洪武十四年),明太祖朱元璋派傅友德、蓝玉、沐英率30万大军征伐云南,消灭了元梁王政权,次年改中庆路为云南府,并筑砖城,周长九里三分(约合今4443米),高二丈九尺二寸(约合今9米),设六门。此后,沐英负责镇守云南。在明代,陆续有大批他地汉族向云南移民,改变了云南的人口结构。
南明永历帝一度入滇,昆明称滇都(或滇京),继续抗清。1659年,吴三桂入滇,永历帝逃往缅甸。1662年6月1日(南明永历十六年或清康熙元年四月十五日),吴三桂绞杀永历帝于昆明。吴三桂因追杀永历而被顺治封为平西王,驻扎云南,在五华山、翠湖一带扩建王府。1673年(康熙十二年),康熙决定削藩,吴三桂在昆明出兵反清。1681年(康熙二十年),清军攻破昆明,吴三桂之孙吴世璠自杀,三藩之乱失败。
300 years later, Ming General Wu Sangui defected to Manchu invaders and held the city until his death in 1678, long after the rest of China had fallen under Manchu rule. During the beginning of Qing rule, the entirety of Yunnan and Guizhou were ruled from Kunming and Wu.[24] During the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, the seat of Wu’s newly declared Zhou dynasty was moved to Hengzhou in Hunan. Later in 1678, when Wu died, his grandson Wu Shifan resisted the Qing for two more months before committing suicide, reverting control of the city back into Qing hands. During the Ming and Qing dynasties, it was the seat of the superior prefecture of Yunnan.
【参考译文】300年后,明朝将领吴三桂投降满清入侵者,并一直占据昆明,直到1678年去世,此时中国其他地区早已落入满清统治之下。在清朝统治初期,整个云南和贵州都是由昆明和吴三桂统治的。[24]在“三藩之乱”期间,吴三桂新建立的周朝都城迁到了湖南的衡州。后来,在1678年吴三桂去世后,他的孙子吴世璠又抵抗了清朝两个月后才自杀,昆明城再次落入清朝之手。在明清时期,昆明是云南府治所在地。
In 1832, the beginnings of a real city were acknowledged within the city walls and there were significant structures within their confines. The founding of the city can therefore be said to have been a predominantly 19th century affair. It was also in this century that the city grew to become the major market and transport centre for the region. [citation needed] Many of the city’s inhabitants were displaced as a result of the 1833 Kunming earthquake.
【参考译文】1832年,城墙内开始显现出真正城市的雏形,城墙内建有许多重要建筑。因此,可以说这座城市主要是在19世纪建立起来的。也正是在这个世纪,昆明发展成为该地区的主要市场和交通中心。[需要引文]1833年昆明地震导致许多市民流离失所。
The rebel leader Du Wenxiu, the Muslim Han Sultan of Dali, attacked and besieged the city several times between 1858 and 1868. A great part of the city’s wealth did not survive the 1856 Panthay Rebellion, when most of the Buddhist sites in the capital were badly damaged, converted to mosques or razed. Decades later, Kunming began to be influenced by the West, especially from the French Empire. In the late 1800s, the French started to build the Kunming-Haiphong railway between Kunming and Haiphong in what was then French Indochina.[25] In the 1890s, an uprising against working conditions on the Kunming–Haiphong rail line saw many laborers executed after France shipped in weapons to suppress the revolt. The meter-gauge rail line, only completed by around 1911, was designed by the French so that they could tap into Yunnan’s mineral resources for their colonies in Indochina.
【参考译文】叛军首领杜文秀,即大理的穆斯林汉人苏丹,在1858年至1868年间多次攻打并围攻昆明。1856年的回民起义让昆明损失了大量财富,当时首都的大部分佛教遗址都遭到了严重破坏,或被改建成清真寺,或被夷为平地。几十年后,昆明开始受到西方的影响,尤其是来自法兰西帝国的影响。19世纪末,法国开始修建昆明至海防的铁路,连接当时属于法属印度支那的昆明和海防。[25]19世纪90年代,昆明至海防铁路线上的工人因恶劣的工作条件而起义,法国运来武器镇压起义,导致许多工人被处决。这条米轨铁路由法国设计,直到1911年前后才建成,目的是开发云南的矿产资源,以供其在印度支那的殖民地使用。
Kunming was a communications center during this time and a junction of two major trading routes, one westward via Dali and Tengchong County into Myanmar, the other southward through Mengzi County to the Red River in Indochina. Eastward, a difficult mountain route led to Guiyang in Guizhou province and thence to Hunan province. To the northeast was a well-established trade trail to Yibin in Sichuan province on the Yangtze River. But these trails were all extremely difficult, passable only by mule trains or pack-carrying porters. [citation needed]
【参考译文】当时,昆明是通讯中心,也是两条主要贸易路线的交汇点,一条向西经大理和腾冲县进入缅甸,另一条向南经蒙自县到达印度支那的红河。向东则是一条艰难的山路,通往贵州省的贵阳,再通往湖南省。向东北则是一条通往四川省长江沿岸宜宾的成熟贸易路线。但这些路线都极其艰难,只有驮队或背夫才能通行。[需要引文]
1.4 近现代
1.4.1 清代之后 | After Qing dynasty
1911年10月30日(农历九月初九日),滇军将领蔡锷、唐继尧在昆明发动重九起义,宣布云南独立。 1915年12月25日, 唐继尧、蔡锷、李烈钧等人宣布云南起义(护国运动),反对袁世凯称帝,编组护国军出师讨伐。
Kunming reverted to county status in 1912, under the name Kunming, and became a municipality in 1935. [citation needed] The opening of the Kunming area began in earnest with the completion in 1906–1910 of the Kunming-Haiphong Railway to Haiphong in north Vietnam (part of French Indochina).
【参考译文】1912年,昆明恢复为昆明县,并于1935年设市。[需要引证]随着1906年至1910年间昆明至越南北部(法属印度支那的一部分)海防的昆河铁路竣工,昆明地区的开放正式开始。
1927年-1945年,滇军首领、国民党人龙云控制云南18年之久,被称为“云南王”。
Kunming became a treaty port opening to foreign trade in 1908 and became a commercial center soon after.[19] A university was set up in 1922. In the 1930s the first highways connected to Kunming were built, linking Kunming with Chongqing in Sichuan and Guiyang in Guizhou to the east.
【参考译文】1908年,昆明成为对外通商的条约口岸,不久后便发展成为商业中心。[19]1922年,当地创办了一所大学。20世纪30年代,昆明修建了首批公路,向东与四川的重庆和贵州的贵阳相连。
The local warlord General Tang Jiyao established the Wujiaba Aerodrome in 1922; an additional 23 airports would be established in Yunnan from 1922 to 1929.[26]
【参考译文】当地军阀唐继尧于1922年修建了巫家坝机场;从1922年至1929年,云南又陆续修建了23座机场。[26]
1.4.2 第二次世界大战(1937-1945)| Second World War (1937–1945)
1937年抗日战争爆发以后,昆明成为“抗日大后方”,外地的许多学校、工厂(如中央机器厂、中央电工厂、军工光学厂、钢铁厂、53兵工厂、电力制钢厂、纺纱厂、烟厂)、银行、商号和难民辗转搬迁昆明。1937年昆明人口为14万多人,到1945年人口增至25万多人。1938年修筑的滇缅公路(长959千米),以及中印驼峰航线,使得昆明成为抗战期间中国接受国际援助的主要通道和物资转往全国各地的中转站,城市受到交通因素的推动,迅速近代化,对后来的城市发展产生深远的影响。1941年到1942年,美国空军援华飞虎队以昆明为基地,对日进行空中作战。同时,北京大学、清华大学和南开大学这三所著名大学也在战时内迁昆明,组成国立西南联合大学,大批著名教授云集昆明。1945年-1946年间,昆明学生反战运动高涨,国民党特务因此造成一二·一惨案、李闻惨案。
Kunming was transformed into a modern city as a result of fighting of the Second Sino-Japanese War/World War II in 1937 with the outbreak of the Battles of Shanghai, Nanking and Taiyuan, forcing a great movement of refugees from the north and eastern coastal regions of China,[28] bringing much commerce and industry into the southwest of China, including Kunming. They carried dismantled industrial plants with them, which were then re-erected beyond the range of Japanese bombers. [citation needed] In addition, a number of universities and institutes of higher education were evacuated there. The increased trade and expertise quickly established Kunming as an industrial and manufacturing base for the wartime government in Chongqing. [citation needed]
【参考译文】1937年,随着上海、南京和太原战役的爆发,中国卷入了第二次中日战争(即第二次世界大战),昆明因此发生了翻天覆地的变化。这场战争迫使中国北部和东部沿海地区的大量难民迁移,[28]为中国西南部地区,包括昆明,带来了大量的商业和工业活动。难民们携带了拆卸下来的工厂设备,这些设备在日本轰炸机轰炸范围之外被重新组装起来。[需要引证]此外,还有许多大学和高等教育机构也被疏散到了昆明。贸易的增长和专业技术的引进迅速确立了昆明作为战时政府所在地重庆的工业和制造业基地的地位。[需要引证]
As the battles of Shanghai, Taiyuan and Nanjing were lost by the end of 1937, and with Wuhan falling into Japanese occupation by the end of 1938, many more of China’s military forces and civilians retreated to cities outside the reach of the Japanese military ground forces a year prior to the outbreak of the Second World War in Europe in 1939, including the relocation of the Chinese Air Force Academy from Jianqiao Airbase to Kunming’s Wujiaba Airbase, where the airfield was vastly expanded, becoming the new training hub for the battered but regrouped Chinese Air Force in which Lieutenant General Claire Lee Chennault took command of cadet training duties in the summer of 1938.
【参考译文】到1937年底,上海、太原和南京战役相继失利,而武汉也在1938年底沦陷于日军的占领之下。在1939年欧洲爆发第二次世界大战前的一年里,中国的许多军队和平民撤退到了日军地面部队鞭长莫及的城市,其中包括将中国空军军官学校从建桥机场迁往昆明的巫家坝机场。巫家坝机场因此大规模扩建,成为遭受重创但重新组建的中国空军的新训练中心。1938年夏,克莱尔·李·陈纳德中将接管了那里的学员训练工作。
The Chinese Air Force command established the 41st Pursuit Squadron based in Kunming, also known as the French Volunteer Group squadron in June 1938, and with them they brought Dewoitine D.510 fighters, with the intention of securing the sale of the planes to the Chinese Air Force; the French participated in some combat engagements against Japanese raids, including dogfights against Mitsubishi A5M fighters with Chinese Hawk III fighters over Nanchang, but after several setbacks, including a fighter pilot KIA, the group was disbanded in October 1938.[29]
【参考译文】1938年6月,中国空军司令部在昆明组建了第41驱逐机中队,又称法国志愿飞行大队中队,并带来了德沃蒂纳D.510战斗机,意图确保将这些飞机出售给中国空军;法国飞行员参与了一些对抗日军空袭的战斗,包括在中国南昌上空用中国霍克III战斗机与三菱A5M战斗机进行的空战,但在遭遇多次挫折,包括一名战斗机飞行员阵亡后,该飞行大队于1938年10月被解散。[29]
Although the Empire of Japan was focusing on ending the Chinese war of resistance at the Battle of Chongqing and Chengdu, Kunming was not out of the reach of Japanese air raids, and faced attacks by IJAAF and IJNAF bombers;[30] military assets and infrastructure were under regular attack, while the RoCAF 18th Fighter Squadron and units of the Air Force Academy at Wujiaba were tasked with aerial defense of Kunming.[31] The city of Kunming was prepared as an alternate National Redoubt in case the temporary capital in Chongqing fell, with an elaborate system of caves to serve as offices, barracks and factories, but it was never utilised. Kunming was to have served again in this role during the ensuing Chinese Civil War, but the Nationalist garrison there switched sides and joined the Communists. Instead, Taiwan would become the last redoubt and home of the Republic of China government, a role it fulfills to this day.[32]
【参考译文】尽管日本帝国正集中精力在重庆和成都战役中结束中国的抗日战争,但昆明并未逃脱日本空军的轰炸范围,并遭受了日本陆军航空队和日本海军航空队轰炸机的袭击;[30]军事资产和基础设施经常遭到袭击,而空军第18战斗机中队和巫家坝空军军官学校的部队则负责昆明的防空任务。[31]昆明被准备作为重庆临时首都沦陷时的备选国家避难所,拥有一个复杂的洞穴系统,用作办公室、营房和工厂,但这一系统从未被使用过。在随后的中国内战中,昆明本应再次发挥这一作用,但当地的国民党驻军倒戈加入了共产党。相反,台湾成为了中华民国政府的最后一个避难所和所在地,至今仍发挥着这一作用。[32]
When the city of Nanning fell to the Japanese during the Battle of South Guangxi, China’s sea-access was cut off. However, the Chinese victory at the Battle of Kunlun Pass kept the Burma Road open. When the Japanese began occupying French Indochina in 1940, the Burma Road that linked Kunming and the outside-world with unoccupied China grew increasingly vital as much of the essential support and materials were imported through Burma. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, and the start of the Pacific War in December 1941, Kunming acted as an Allied military command center, which grouped the Chinese, American, British and French forces together for operations in Southeast Asia. Kunming became the northern and easternmost terminus of the vital war-supply line into China known as “The Hump‘, which stretched over the Himalayas from British bases in India to port-of-entry Kunming. The Office of Strategic Services‘ Service Unit Detachment 101 (predecessor to the 1st Special Forces Group) was also headquartered in Kunming. Its mission was to divert and disrupt Japanese combat operations in Burma.[33]
【参考译文】当南宁在南桂战役中沦陷于日军之手时,中国的海上通道被切断。然而,中国军队在昆仑关战役中取得的胜利保持了滇缅公路的畅通。1940年,当日军开始占领法属印度支那时,连接昆明和外界以及未被占领的中国的滇缅公路变得越来越重要,因为大部分必需的支持和物资都是通过缅甸进口的。1941年12月,珍珠港事件爆发,太平洋战争开始,昆明成为盟军军事指挥中心,将中国、美国、英国和法国的军队集结在一起,共同在东南亚开展行动。昆明成为了进入中国的重要战争补给线“驼峰航线”最北端和最东端的终点,这条航线从英国在印度设立的基地横跨喜马拉雅山,抵达进入中国的门户昆明。战略情报局第101勤务分队(第一特种部队的前身)的总部也设在昆明。其任务是转移和破坏日军在缅甸的战斗行动。[33]
Kunming, the northern terminus of all three of the Burma Road, the Ledo Road, and The Hump supply-line, was increasingly targeted by the IJAAF. When the Burma Road was lost to the Japanese, the Hump became China’s primary lifeline to the outside world. The 1st American Volunteer Group, known as the “Flying Tigers“, was based in Kunming and tasked with defense of The Hump supply-line against Japanese aerial interceptions.[34]
【参考译文】昆明是滇缅公路、利多公路和驼峰航线这三条供应线的北端终点,因此越来越成为日本陆军航空队的目标。当滇缅公路沦陷于日军之手时,驼峰航线成为了中国通往外界的主要生命线。第一美国志愿飞行队,又称“飞虎队”,以昆明为基地,负责防御驼峰航线免受日军的空中拦截。[34]
Further information: Battle of Yunnan-Burma Road【更多信息:滇缅公路战役】
Industry became important in Kunming during World War II. The large state-owned Central Machine Works[35] was transferred there from Hunan, while the manufacture of electrical products, copper, cement, steel, paper, and textiles expanded.
【参考译文】在第二次世界大战期间,工业在昆明变得重要起来。大型国有中央机器厂[35]从湖南迁至昆明,同时,电子产品、铜、水泥、钢铁、纸张和纺织品的制造业也得到了扩展。
1.4.3 第二次世界大战后 | After World War II
第二次国共内战末期的1949年12月9日,云南省主席卢汉在昆明宣布转投共产党,昆明市市长裴存藩逃往台湾,云南政权和平转移。1950年3月28日,昆明市人民政府宣布成立,潘朔端任市长。
Until 1952, Kunming was a walled city. The city government in 1952 ordered hundreds of young people to tear down the wall and use its bricks to make a new road running north–south. To show its appreciation for the young people that demolished the east wall, the city government named the new street, Qingnian Lu, after them. The existence of the walls still echoes today at place names like the district of Xiaoximen (小西门; ‘Lesser West Gate’) and Beimen Jie (北门街; ‘North Gate Street’). There are also less obvious connections to the wall, such as Qingnian Lu (青年路; ‘Youth Road’), in the location of Kunming’s east wall.
【参考译文】直到1952年,昆明还是一座有城墙的城市。1952年,市政府下令数百名年轻人拆除城墙,并用城墙的砖石修建一条南北走向的新路。为了感谢拆除东城墙的年轻人,市政府将这条新路命名为“青年路”(Qingnian Lu)。城墙的存在至今仍在一些地名中有所体现,如小西门区(Xiaoximen,意为“小西门”)和北门街(Beimen Jie,意为“北门街”)。此外,在昆明东城墙原址上的青年路(Qingnian Lu,意为“青年路”)也与城墙有着不那么明显的联系。
After 1949, Kunming developed rapidly into an industrial metropolis with the construction of large iron and steel and chemical complexes, along with Chongqing, Chengdu and Guiyang in the southwest. A Minorities’ Institute was set up in the 1950s to promote mutual understanding and access to university education among Yunnan’s multiethnic population. The city consolidated its position as a supply depot during the Vietnam War and subsequent border clashes. Until Mao Zedong’s death, in much of the rest of the country Kunming was still generally thought as a remote frontier settlement. Accordingly, the government utilized Kunming as a place where to exile people who had fallen politically out of favor, especially during the Cultural Revolution.
【参考译文】1949年以后,随着大型钢铁和化工综合体的建设,昆明与西南地区的重庆、成都和贵阳一起,迅速发展成为一座工业大都市。20世纪50年代,云南设立了民族学院,以促进云南多民族人口之间的相互理解和接受大学教育。在越南战争和随后的边境冲突期间,昆明巩固了其作为物资补给基地的地位。直到毛泽东去世,在中国的大部分其他地区,昆明仍普遍被视为一个偏远的边疆城镇。因此,政府利用昆明作为流放政治上失意的人的地方,尤其是在文化大革命期间。
In 1957, Kunming’s rail link to Haiphong and Hanoi was re-opened (after being cut during World War II). It was cut again in 1979 and re-opened again in 1996.
【参考译文】1957年,昆明至海防和河内的铁路线重新开通(该线路在二战期间被切断)。1979年,该线路再次被切断,并于1996年重新开通。
Since the economic reforms of the mid-1980s, Kunming has enjoyed increased tourism and foreign investment. Several Thai Chinese banks have offices in Kunming, for example, Kasikorn Bank and Krung Thai Bank. Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Thailand has visited Kunming many times to study Chinese culture and promote friendly relations. [citation needed]
【参考译文】自20世纪80年代中期经济改革以来,昆明的旅游业和外国投资不断增加。几家泰籍华人银行在昆明设有办事处,例如开泰银行和泰京银行。泰国玛哈扎克里·诗琳通公主曾多次访问昆明,以学习中国文化并促进友好关系。[需要引文]
In the 1980s and 1990s, the city center was rebuilt, with Swiss help, in its current ‘modern’ style to impress visitors attending the 1999 World Horticultural Exposition.[36] It was primarily during 1997 and 1998 that much of the city’s roads, bridges and high rises were built. The World Horticultural Expo was widely regarded as a public relations success for Kunming.[citation needed] Today the after-effects of the Expo are apparent in more than just the physical improvements to the city—it was the Expo that made the outside world take notice of Kunming, which was relatively unknown at the time.[dubious – discuss]
【参考译文】20世纪80年代和90年代,在瑞士的帮助下,昆明市中心按照当前的“现代”风格进行了重建,以期给参加1999年世界园艺博览会的游客留下深刻印象。[36]主要是在1997年和1998年期间,昆明的大部分道路、桥梁和高楼大厦得以建成。世界园艺博览会普遍被认为是昆明公关活动的一次成功。[需要引文]如今,博览会的影响不仅体现在城市物质条件的改善上,更重要的是,正是这次博览会让世界注意到了当时相对默默无闻的昆明。[有争议——待讨论]
In July 2005, the second Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) Summit was held in Kunming, with government leaders from China, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam participating. There, China agreed to lend its neighbors more than $1 billion for a series of projects. China promoted GMS cooperation as a first step toward building an eventual China-ASEAN Free Trade Area.
【参考译文】2005年7月,第二次大湄公河次区域(GMS)峰会在昆明举行,来自中国、老挝、缅甸(Burma)、泰国、柬埔寨和越南的政府领导人参加了会议。会上,中国同意向邻国提供超过10亿美元的贷款,用于一系列项目。中国将推动大湄公河次区域合作视为建立中国-东盟自由贸易区的第一步。
Infrastructure improvements were underway to improve links between Kunming and Southeast Asia in time for the 2010 establishment of the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area. The FTA made Kunming a trade and financial center for Southeast Asia. In addition to physical improvements to enhance Kunming’s trade with Southeast Asia, the central and provincial governments have made financial preparations to assist the city’s emergence. At the end of 2004, the central government approved Kunming to be one of the 18 mainland cities in which foreign banks could conduct business in renminbi. [citation needed]
【参考译文】为了配合2010年中国-东盟自由贸易区的建立,昆明与东南亚之间的基础设施改善工作正在进行中。自由贸易区使昆明成为东南亚的贸易和金融中心。除了进行物质条件的改善以促进昆明与东南亚的贸易外,中央和省政府还进行了资金准备,以协助昆明的崛起。2004年底,中央政府批准昆明成为18个允许外资银行经营人民币业务的大陆城市之一。[需要引文]
In July 2006, talks at the ASEAN Regional Forum, China, Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma) agreed to construct a highway from Kunming to Chittagong through Mandalay for trade and development.[37]
【参考译文】2006年7月,在东盟地区论坛、中国、孟加拉国和缅甸(Burma)的会谈中,各方同意修建一条从昆明经曼德勒至吉大港的高速公路,以促进贸易和发展。[37]
2014年3月1日晚21时12分,五名新疆独立运动恐怖分子持刀冲入昆明站砍杀路人。随后大批民警赶至现场,四名嫌犯被当场击毙,其余一名嫌犯被击伤。恐袭事件发生于21时12分,但直到23时还有人求救,警方起初没有估计到事件的严重性,未能及时以反恐级别安排警力处理事件。这次事件发生后造成31人死亡,142人受伤。“3·01”事件定性为严重暴力恐怖事件。[4][5][6]
2021年10月11日至15日,2020年联合国生物多样性大会第一阶段会议在昆明举行[7]。
2022年5月,昆明市托管西双版纳傣族自治州勐腊县磨憨镇及中国老挝磨憨-磨丁经济合作区(中方区域)。[8][9]
2. 地理 | Geography
昆明地处云贵高原中部,市中心海拔1,891米。南濒滇池,三面环山。
昆明市域总面积约21473平方公里,其中市区建成区面积约460平方公里。
Kunming is located in east-central Yunnan province. It is located between north latitude 24°23′ and 26°22′ N, and east longitude 102°10′ and 103°40′ E, with a total area of 21,600 square kilometres (8,340 square miles). Its widest stretch from the east to the west amounts to 140 kilometres (87 miles) and its largest expansion from the north to the south amounts to 220 kilometres (137 miles).
【参考译文】昆明位于云南省中东部,地处北纬24°23′至26°22′、东经102°10′至103°40′之间,总面积为21,600平方公里(8,340平方英里)。其东西最大横距140公里(87英里),南北最大纵距220公里(137英里)。
Situated in a fertile lake basin on the northern shore of the Lake Dian and surrounded by mountains to the north, west, and east, Kunming has always played a pivotal role in the communications of southwestern China. Lake Dian, known as “the Pearl of the Plateau”, is the largest lake in Yunnan and the sixth largest fresh water lake in China. It has an area of approximately 340 square kilometres (130 square miles). Kunming’s highest point is Mazong Ridge of the Jiaozi Snow Mountain in Luquan with an elevation of 4,247 metres (13,934 feet), and its lowest point is the joint of the Xiao River and the Jinsha River in Dongchuan District, with an elevation of 695 metres (2,280 feet). Its downtown area is 1,891 metres (6,204 feet) above sea level.
【参考译文】昆明坐落在滇池北岸的肥沃湖盆上,北、西、东三面环山,在中国西南地区一直发挥着重要的交通枢纽作用。滇池被誉为“高原明珠”,是云南省最大的湖泊,也是中国第六大淡水湖,面积约为340平方公里(130平方英里)。昆明的最高点位于禄劝县的轿子雪山马鬃岭,海拔4,247米(13,934英尺),最低点位于东川区小江与金沙江交汇处,海拔695米(2,280英尺)。其市中心海拔为1,891米(6,204英尺)。
About 96 km (60 mi) southeast of the city centre is the Stone Forest in Shilin County, a karst formation developed as a tourist attraction consisting of rock caves, arches, and pavilions. It is part of the larger karst-based landscape of the area.
【参考译文】距离市中心约96公里(60英里)的东南方向,是石林彝族自治县的石林,这是一片由岩溶地貌形成的旅游景区,包括岩洞、石拱和亭台等景观,是当地更大范围的岩溶地貌景观的一部分。
2.1 气候 | Climate
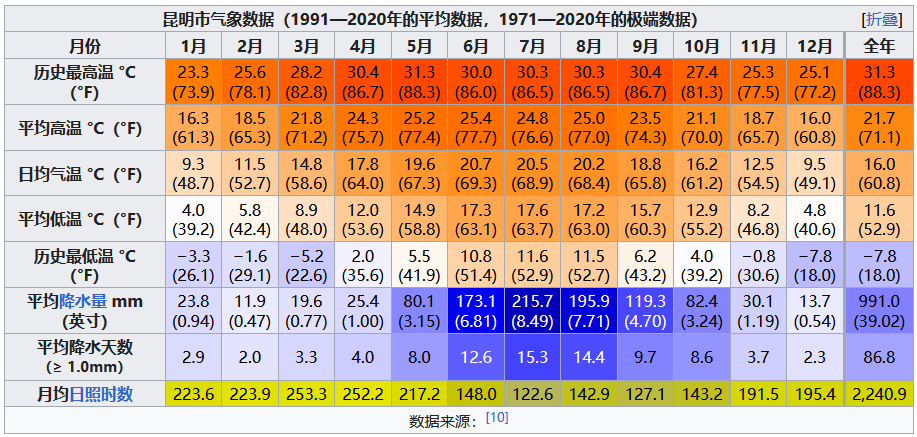
Located at an elevation of 1,890 metres (6,200 feet) on the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau with low latitude and high elevation, Kunming has one of the mildest climates in China, characterized by short, cool dry winters with mild days and crisp nights, and long, balmy and humid summers. With its perpetual spring-like weather which provides the ideal climate for plants and flowers, Kunming is known as the “City of Eternal Spring”.[39] The weather has seldom reached high temperatures in summer, only exceeding 30 °C (86 °F) on a handful of occasions. However, freak snowfalls occur in occasional winters. Controlled by a subtropical highland climate (KöppenCwb), the monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 8.9 °C (48.0 °F) in January to 20.3 °C (68.5 °F) in June, with daily high temperatures reaching their lowest point and peak in December and May, respectively.
【参考译文】昆明位于云贵高原,海拔1890米(6200英尺),纬度低而海拔高,拥有中国最温和的气候之一。其特点为冬季短、凉爽干燥,白天温和夜晚清爽;夏季长、温暖潮湿。昆明四季如春,为植物和花卉提供了理想的气候,因此被称为“春城”。[39]夏季气温很少达到高温,仅少数情况下会超过30°C(86°F)。然而,偶尔在冬季也会出现异常降雪。昆明受亚热带高原气候(KöppenCwb)控制,月平均气温范围从1月的8.9°C(48.0°F)到6月的20.3°C(68.5°F),日最高气温的最低点和最高点分别出现在12月和5月。
The city is covered with blossoms and lush vegetation all-year round.[40] The period from May to October is the monsoon season and the rest of the year is dry. The city has an annual mean temperature of 15.52 °C (59.9 °F), rainfall of 979 millimetres (38.5 in) (nearly three-fifths occurring from June to August) and a frost-free period of 230 days. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 30% in July to 69% in February and March, the city receives 2,198 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extreme temperatures in the city have ranged from −7.8 to 32.9 °C (18 to 91 °F) on 29 December 1983 and 25 May 2014 respectively.
【参考译文】昆明全年鲜花盛开,植被茂盛。[40]5月至10月为雨季,其余时间为旱季。昆明年平均气温为15.52°C(59.9°F),年降水量为979毫米(38.5英寸)(其中近五分之三集中在6月至8月),无霜期为230天。7月日照百分率最低,为30%,2月和3月最高,为69%,全年日照时间为2198小时。该市极端气温范围在-7.8°C至32.9°C(18°F至91°F)之间,分别出现在1983年12月29日和2014年5月25日。
2.2 自然资源 | Natural resources
Mineral resources include phosphorus, salt, magnesium, titanium, coal, quartz sand, clay, silica, copper. Phosphorus and salt mines are the most plentiful. Kunyang Phosphorus Mine is one of the three major phosphorus mines in the country. Rock salt reserves are 1.222 billion tonnes (1.203 billion long tons; 1.347 billion short tons) and mirabilite reserves are 1.908 billion tonnes (1.878 billion long tons; 2.103 billion short tons). Dongchuan is a major copper production base.
【参考译文】矿产资源包括磷、盐、镁、钛、煤、石英砂、粘土、硅石、铜等。其中磷矿和盐矿最为丰富。昆阳磷矿是全国三大磷矿之一。岩盐储量达12.22亿吨(12.03亿长吨;13.47亿短吨),芒硝储量达19.08亿吨(18.78亿长吨;21.03亿短吨)。东川是主要的铜生产基地。
Proven reserves of Coal bed gas is about 500 billion cubic metres (18,000 billion cubic feet), equal to 720 million tonnes (710 million long tons; 790 million short tons) of standard coal.[44] Geothermal resources are widely distributed.
【参考译文】已探明的煤层气储量约为5000亿立方米(1.8万亿立方英尺),相当于7.2亿吨(7.1亿长吨;7.9亿短吨)标准煤。[44]地热资源分布广泛。
2.3 环境与园艺 | Environment and horticulture
Kunming has 2,585 hectares (6,390 acres) of lawns, trees and flowers, averaging 4.96 square metres (53.4 square feet) per capita and a green space rate of 21.7 percent. The city’s smoke control area is 115 square kilometres (44 square miles) and noise control area 87 square kilometres (34 square miles). [citation needed]
【参考译文】昆明拥有2585公顷(6390英亩)的草坪、树木和花卉,人均绿地面积达到4.96平方米(53.4平方英尺),绿化覆盖率达21.7%。该市的烟尘控制区面积为115平方公里(44平方英里),噪声控制区面积为87平方公里(34平方英里)。[需要引文]
Kunming is a significant horticultural center in China, providing products such as grain, wheat, horsebeans, corn, potato and fruit such as peaches, apples, oranges, grapes and chestnuts. [citation needed] Kunming is world-famous for its flowers and flower-growing exports. More than 400 types of flowers are commonly grown in Kunming. The camellia, Yulan magnolia, azalea, fairy primrose, lily and orchid are known as the six famous flowers of the city.
【参考译文】昆明是中国重要的园艺中心,提供粮食、小麦、蚕豆、玉米、土豆等农产品,以及桃子、苹果、橘子、葡萄和板栗等水果。[需要引文]昆明因其花卉种植和花卉出口而举世闻名。昆明常见的花卉种类超过400种。山茶花、白玉兰、杜鹃花、报春花、百合花和兰花被誉为昆明的六大名花。
The camellia was confirmed by the Municipality of Kunming as its city flower in 1983.
【参考译文】1983年,昆明市政府正式将山茶花定为市花。
The Kunming city government plans to create an environmental trial court to deal with environment-related lawsuits. It is to be part of the city’s intermediate people’s court and will have jurisdiction over appeals by companies that have been found guilty of violating environmental laws in cities throughout Yunnan.[45]
【参考译文】昆明市政府计划设立环境审判法庭,以处理与环境相关的诉讼案件。该法庭将成为市中级人民法院的一部分,并将对在云南省各城市中被判定违反环境法的公司提起的上诉具有管辖权。[45]
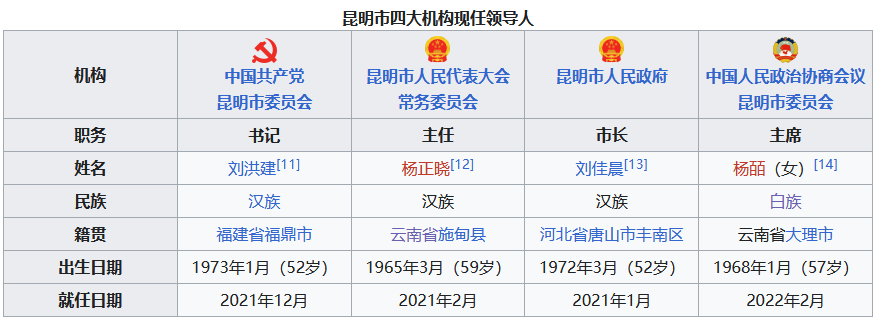
3. 政治
3.1 现任领导
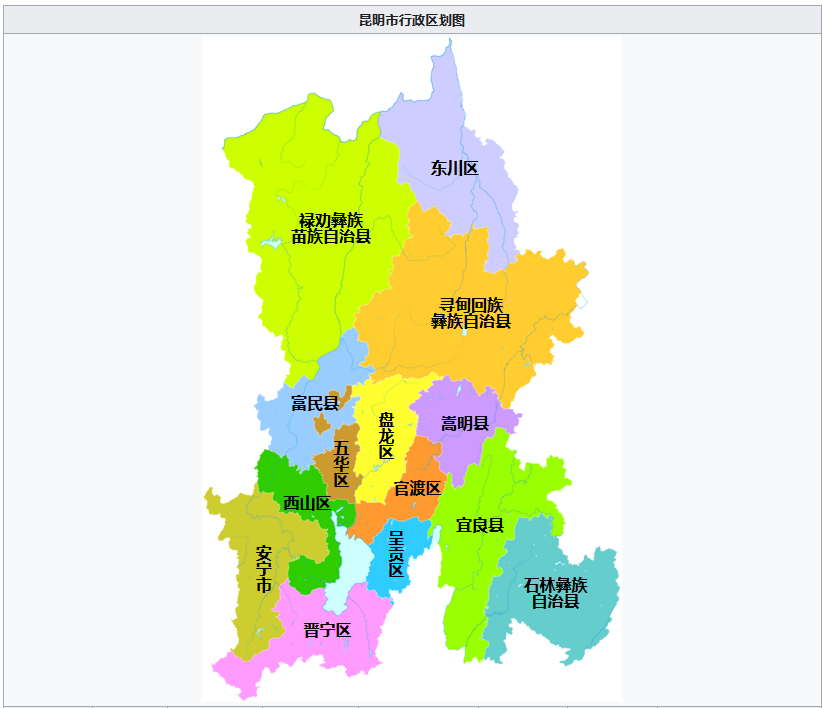
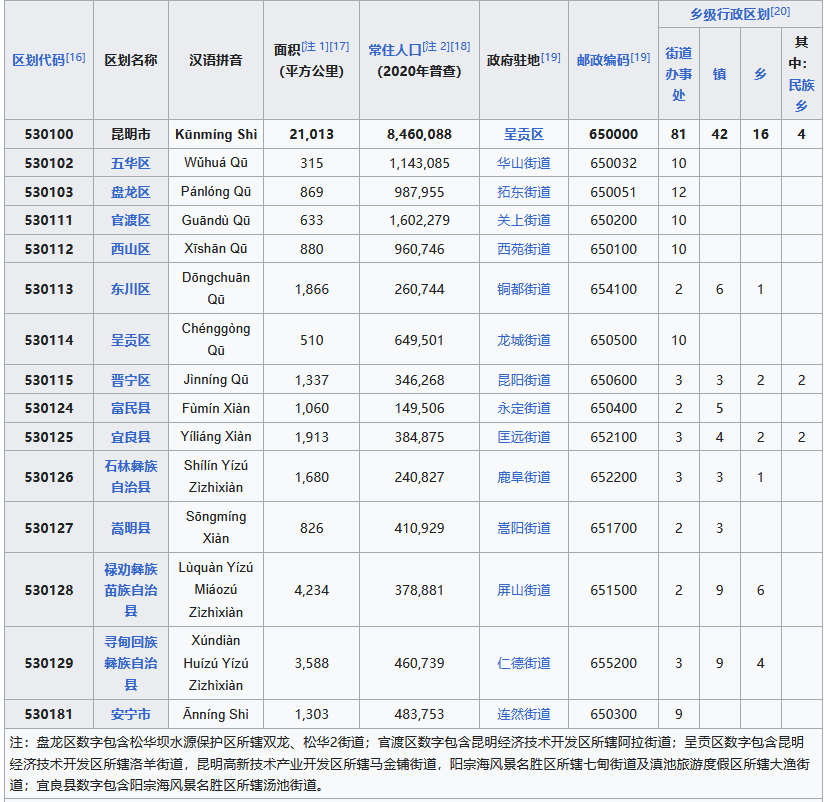
3.2 行政区划 | Administrative divisions
昆明市托管玉溪市澄江市阳宗镇,与西双版纳州合作共建勐腊县磨憨镇[15]。
除正式行政区划外,昆明市还设立以下行政管理区:国家级昆明经济技术开发区、国家级昆明高新技术产业开发区、昆明滇池国家旅游度假区、昆明阳宗海风景名胜区、中国老挝磨憨—磨丁经济合作区。

3.3 公共安全和犯罪 | Public security and crime
The headquarters of the Kunming Municipal Public Security Bureau is on Beijing Lu. Its foreign affairs department, located on Jinxing Huayuan, Jinxing Xiao Lu in the northeast of the city, handles immigration and travel visas.[74]
【参考译文】昆明市公安局总部位于北京路。其外事部门位于该市东北部的金星花园金星小路,负责处理移民和旅行签证事务。[74]
毒品走私 | Drug trafficking
See also: Illegal drug trade in China【另见:中国非法毒品贸易】
Kunming has a pivotal role as a major conduit point in international drug trafficking as it is the closest major Chinese city to the Golden Triangle in Southeast Asia. The Kunming Municipal Public Security Bureau Narcotics Squad is the specialist counter-narcotics police service.
【参考译文】昆明在国际毒品走私中扮演重要角色,是连接东南亚金三角地区与中国的主要通道,因为金三角地区是中国距离最近的大型毒品产地。昆明市公安局禁毒支队是专业的缉毒警察队伍。
Police confiscated at least three tons of drugs in Yunnan in 2005. Yunnan province seized 10 tons of illegal drugs in 2006, accounting for 80 percent of the total drugs confiscated nationwide during the period, according to Sun Dahong, then deputy director of Yunnan’s provincial Public Security Bureau. The total is more than double the amount seized in the province in 2005.[75]
【参考译文】据时任云南省公安厅副厅长的孙大虹介绍,2005年,云南警方缴获毒品至少3吨。2006年,云南省缴获毒品10吨,占全国同期缴获毒品总量的80%,是2005年缴获量的两倍多。[75]
Heroin and methamphetamine seem to be the main targets of the 30,000+ strong anti-drug police in Yunnan. The majority of heroin coming into China from the Golden Triangle passes through Dali[citation needed] from where it is then distributed to the rest of China and internationally via China’s coastal cities.
【参考译文】海洛因和冰毒似乎是云南3万多名缉毒警察的主要打击目标。从金三角进入中国的大部分海洛因都要经过大理[需要引文],然后再通过中国的沿海城市分销到国内其他地方和国际市场。
Kunming Municipal Compulsory Rehabilitation Center in Kunming is the main rehabilitation center for drug addicts, mostly recovering from heroin addiction. International drug rings have used Yunnan and Kunming to channel new synthetic drugs (like methamphetamine) as well as traditional drugs like heroin.
【参考译文】昆明市强制戒毒康复中心是昆明主要的戒毒康复中心,主要针对海洛因成瘾者进行康复。国际贩毒集团利用云南和昆明贩卖新型合成毒品(如冰毒)以及传统毒品(如海洛因)。
Opium was until recently in widespread medicinal use by many of the minority peoples of the province; however, after the Opium War the Chinese government has made growing the poppy illegal, and all but stamped out its production within the borders of Yunnan.[citation needed]
【参考译文】直到最近,鸦片仍在云南省许多少数民族中广泛使用作为药物;然而,鸦片战争后,中国政府宣布种植罂粟为非法行为,并几乎在云南境内彻底消灭了罂粟的种植。[需要引文]
4. 人口 | Demographics
2022年末,昆明市常住人口为860.0万人[21],比2021年末增加9.8万人,增长1.2%。2022年常住人口中,城镇常住人口为697.5万人,乡村常住人口为162.5万人,常住人口城镇化率为81.1%,比2021年末提高0.6个百分点。
根据2020年第七次全国人口普查,全市常住人口为8,460,088人[22]。同第六次全国人口普查的6,432,209人相比,十年共增加了2,027,879人,增长31.53%,年平均增长率为2.78%。其中,男性人口为4,327,987人,占总人口的51.16%;女性人口为4,132,101人,占总人口的48.84%。总人口性别比(以女性为100)为104.74。0-14岁的人口为1,267,713人,占总人口的14.98%;15-59岁的人口为5,974,188人,占总人口的70.62%;60岁及以上的人口为1,218,187人,占总人口的14.4%,其中65岁及以上的人口为887,222人,占总人口的10.49%。居住在城镇的人口为6,740,458人,占总人口的79.67%;居住在乡村的人口为1,719,630人,占总人口的20.33%。
4.1 民族
全省的26个民族都有部分在昆明居住,全市人口平均预期寿命76岁。
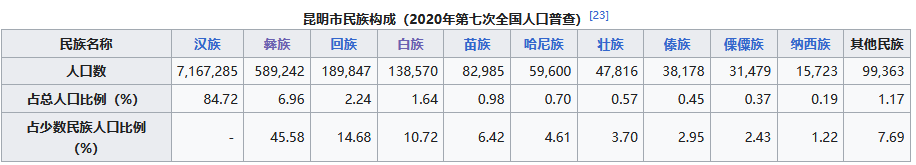
全市常住人口中,汉族人口为7,167,285人,占84.72%;各少数民族人口为1,292,803人,占15.28%。与2010年第六次全国人口普查相比,汉族人口增加1,624,891人,增长29.32%,占总人口比例下降1.45个百分点;各少数民族人口增加402,988人,增长45.29%,占总人口比例增加1.45个百分点。
4.2 宗教
5. 交通 | Transport
昆明市是云南省的交通枢纽,是中国面向东南亚的口岸。
Kunming is situated on the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. Rail and air are the main two methods to travel to or from Kunming from outside Yunnan.
【参考译文】昆明位于云贵高原上。从云南省外前往昆明或从昆明出发,铁路和航空是主要的两种交通方式。
5.1 铁路 | Rail
昆明的第一条铁路是法国修筑的滇越铁路(今称昆河铁路),通往越南,1910年通车。铁轨宽度为一米,故为米轨铁路。直到1966年以前,这条铁路一直是昆明与外界联系的主要通道,昆明也成为中国唯一一个“火车不通国内通国外”的省会城市,被称为“云南十八怪”之一。昆河铁路目前是中国唯一一条米轨铁路,起点站昆明北站位于昆明市区北部,曾经每天有一班列车开往中越边境的河口,每周有两班列车开往越南首都河内。目前该铁路以货运为主,客运已基本停止,仅存王家营经昆明北至石咀的市郊列车,上午、下午各一趟。由于地铁四号线的修建,米轨列车8861/2/3/6/9/8870次停止运营[24]。上午的列车由昆明北站发车,开往王家营,然后由王家营经昆明北开往石咀,而后返回昆明北站。下午的列车仅由昆明北往返王家营。
1966年以后,从昆明通往外省的数条铁路陆续通车,包括贵昆铁路(1966年通车,全长640公里)、成昆铁路(1970年通车,全长1100公里)、内昆铁路、南昆铁路(全长900公里)等;此外还修筑了省内线路如广通至大理的广大铁路、昆明到玉溪的昆玉铁路。并将在日后作为泛亚铁路南路终点。2016年12月28日,沪昆客运专线和南昆客运专线全线开通,标志着云南正式迈入高铁时代。
Kunming has three major railway stations:
【参考译文】昆明有三大火车站:
- Kunming railway station is at the southern end of Beijing Xi Lu. Compared with the other railway station (North Railway Station), Kunming Railway Station services most of the “conventional” (not high-speed) trains to places to other provinces of China. Trains run north to Chengdu, southeast via Xingyi to Baise and Nanning in Guangxi, and east through Guizhou, via Liupanshui, Anshun, Guiyang, into the rest of the country.
【参考译文】昆明站位于北京路南端。与其他火车站(如昆明北站)相比,昆明站主要服务于开往中国其他省份的“常规”(非高速)列车。列车可向北开往成都,向东南经兴义开往广西百色和南宁,或向东经六盘水、安顺、贵阳开往中国其他地区。 - Kunming South railway station, opened at the end of 2016, is located in Chenggong District, many miles southeast from the historical city center. It is the western terminal of the Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway and the Guangzhou–Nanning–Kunming high-speed railway, and has high-speed service to destinations along these lines and elsewhere on the nation’s high-speed network.
【参考译文】昆明南站于2016年底开通,位于呈贡区,距历史城区中心数英里远。它是沪昆高速铁路和广南昆高速铁路的西端终点站,并沿这些线路以及中国其他高速铁路网提供高速列车服务。 - Kunming North railway station (serviced by the No. 23 Bus) is on the heritage 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) metre gauge Kunming–Hai Phong Railway, which runs to Hekou and Vietnam. Most of the station has been converted into a museum. Due to the deterioration of the railway line, the long distance narrow-gauge service has been cancelled; however, as of 2012, some local narrow gauge service still operates at Kunming North Railway Station, in particular two daily trains to Shizui (石咀) Station on the western outskirts of Kunming, and to Wangjiaying (王家营) east of the city.[58]
【参考译文】昆明北站(23路公交车可达)服务于历史悠久的1000毫米(3英尺3又3/8英寸)窄轨昆明-海防铁路,该铁路通往河口和越南。该站大部分区域已被改造成博物馆。由于铁路线路状况恶化,长途窄轨列车服务已被取消;然而,截至2012年,昆明北站仍提供一些窄轨列车服务,特别是每天两班开往昆明西郊石咀站和昆明以东王家营站的列车。[58]
As of 2017, railway development projects continue to proceed in the Kunming metropolitan area. In February 2017, the railway authorities announced that a connector between the new Kunming South railway station and the old Kunming railway station (also known as the Nanyao Station; 南窑火车站) will open by the end of 2017, making it possible for some high-speed train to serve Kunming railway station as well.[59]
【参考译文】截至2017年,昆明都市区的铁路建设项目仍在继续。2017年2月,铁路部门宣布,连接新建昆明南站和旧昆明站(又称南窑火车站)的连接线将于2017年底开通,这意味着一些高速列车也将服务于昆明站。[59]
5.1.1 地铁计划 | Urban rail plan
See also: Kunming Metro / 主条目:昆明地铁
In May 2010, Kunming began construction on its first urban rail lines, line 1 and 2 of the Kunming Metro. An elevated test section had been under construction since 2009. Parts of lines 1 and 2 opened in April 2014.[60] Construction on line 3 began in August 2010 and the Phase 1 was completed in 2018. The entire system consisting of 6 lines and covering a total of 162 kilometres (101 miles) is estimated to be complete by 2018.
【参考译文】2010年5月,昆明开始建设其首条城市轨道交通线路——昆明地铁1号线和2号线。自2009年起,一段高架试验段已开始建设。1号线和2号线的部分路段于2014年4月开通。[60]3号线的建设始于2010年8月,一期工程于2018年完成。预计整个系统由6条线路组成,总长162公里(101英里),将于2020年前全面建成。
昆明地铁6号线于2012年6月28日开通运营,昆明成为继重庆、成都、西安之后,中国西部地区第四座开通地铁的城市。昆明地铁6号线一期工程连接昆明市区东部的东部汽车站至长水机场航站楼地下的机场中心站,站厅位于航站楼B2层。6号线一期工程线路全长18.018公里,其中地下段长7.76公里,高架段长7.633公里。全线设站4座,其中高架车站1座,地下车站3座。其中大板桥站与机场前站暂不办客。一期工程于2010年3月开工建设,于2012年2月6日开始空载试运行。首末班时间为每天9:00至18:00,发车间隔时间约25分钟,单程运行时间23分钟,单程票价5元。于2020年9月23日开通运营二期工程(东部汽车站至塘子巷站),全线开通。
此外,昆明于2013年5月20日开通了昆明地铁1号线。并于2014年4月30日开通地铁2号线,地铁一二号线贯通主城南北成为西南地区和整个西部第二个同时有3条线路运营的城市。昆明也在2017年8月29日开通昆明地铁3号线(东部汽车站–西山公园)。2020年9月23日,昆明地铁4号线开通运营,其标识色为橙黄色。4号线西起普吉,南至昆明南火车站(高铁站),串联起西北的国家高新技术产业开发区、主城中心区、主城东南的国家经济技术开发区,并向南连接呈贡新城。昆明地铁4号线工程全长43.4千米,共设29座车站、2个停车场、1个车辆段,新建1个主变电站。2022年1月15日,昆明地铁5号线正式开启空载试运行。全长26.45千米,贯穿盘龙区、五华区、西山区、滇池度假区和官渡区,途经世博园片区、圆通公园片区、会展中心片区。
5.1.2 高铁计划 | High-speed rail plan
Kunming will be the hub and terminus for the “Pan Asia High Speed Network” using high-speed trains to connect China, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore.[61]
【参考译文】昆明将成为“泛亚高铁网络”的枢纽和终点站,该网络将通过高铁连接中国、柬埔寨、老挝、缅甸、泰国、马来西亚和新加坡。[61]
Completed but under trial high-speed railways:
【参考译文】已建成但正在试运行的高速铁路:
- Kunming–Shanghai. The construction completed on 16 June 2016. It goes through 6 provincial capital cities: Shanghai, Hangzhou, Nanchang, Changsha, Guiyang and Kunming. The overall length is 2,266 kilometres (1,408 miles). As estimated it would take 3 hours from Shanghai to Nanchang, 2.5 hours from Hangzhou to Nanchang, 4 hours from Kunming to Changsha, 8 hours from Kunming to Hangzhou and 9 hours from Shanghai to Kunming. It is expected to start operating on 30 December 2016.
【参考译文】昆明至上海。该线路于2016年6月16日建成。它途经上海、杭州、南昌、长沙、贵阳和昆明6个省会城市,总长度为2266公里(1408英里)。据估算,从上海到南昌需3小时,从杭州到南昌需2.5小时,从昆明到长沙需4小时,从昆明到杭州需8小时,从上海到昆明则需9小时。预计将于2016年12月30日开始运营。
Construction is underway for the following high-speed railways:
【参考译文】正在建设的高速铁路:
- Kunming–Shanghai. The speed will be 350 km/h (220 mph).
【参考译文】昆明至上海(另一条线路或升级现有线路),设计时速为350公里/小时(220英里/小时)。 - Kunming–Nanning. The speed will be 200 km/h (120 mph). Later the speed may be improved to 250 km/h (160 mph) or 156 miles/h.
【参考译文】昆明至南宁,设计时速为200公里/小时(120英里/小时),未来可能会提速至250公里/小时(160英里/小时)或156英里/小时。 - Kunming–Vietnam via Honghe Prefecture.
【参考译文】昆明经红河州至越南。 - Kunming–Singapore via Laos, Thailand, and Malaysia.
【参考译文】昆明经老挝、泰国和马来西亚至新加坡。
Study or planning is being done for the following railways:
【参考译文】正在研究或规划中的铁路:
- Kunming–Chengdu. The speed will be 250 km/h (160 mph).
【参考译文】昆明至成都,设计时速为250公里/小时(160英里/小时)。 - Kunming–Chongqing. The speed will be 350 km/h (220 mph).
【参考译文】昆明至重庆,设计时速为350公里/小时(220英里/小时)。 - Intercity rail will connect three neighboring cities: Qujing, Chuxiong, and Yuxi. The line to Chuxiong will then be extended to Dali. The speed will be 250 km/h (160 mph).
【参考译文】城际铁路将连接曲靖、楚雄和玉溪三个相邻城市。通往楚雄的线路随后将延伸至大理,设计时速为250公里/小时(160英里/小时)。 - Kunming to Kolkata, India via Myanmar
【参考译文】昆明经缅甸至印度加尔各答。 - Kunming to Kyaukphyu, Myanmar.[62]
【参考译文】昆明至缅甸皎漂。[62]
5.2 航空 | Air transport
Main articles: Kunming Changshui International Airport and Kunming Wujiaba International Airport
【主条目:昆明长水国际机场和昆明巫家坝国际机场】
2012年6月28日,昆明长水国际机场启用,同日昆明原机场昆明巫家坝国际机场停用。昆明长水国际机场是中国面向东南亚、南亚和连接欧亚的国家门户枢纽机场。昆明长水国际机场是国家“十一五”期间的重点建设工程、云南省特大型城市基础设施建设工程、云南省二十项重点工程之一。昆明长水国际机场场址位于云南省昆明市官渡区长水村附近,在昆明市东北方向,距市中心直线距离约24.5公里。近期规划为满足2020年旅客吞吐量3800万人次、货邮吞吐量95万吨、飞机起降30.3万架次的需求建设。远期规划控制用地约22.97平方公里。昆明长水国际机场本期新建两条长度平行跑道,长4000米,60米宽,机场飞行区等级为按照4F能够起降并停靠全球载客量最大的客机空客A380。长水机场有飞往曼谷、悉尼、新加坡、吉隆坡、首尔、河内、胡志明市、仰光、万象、清迈、迪拜、曼德勒、巴黎、温哥华、大阪、名古屋、达卡、科伦坡、马累等国际航线,通往香港、澳门、台北的地区际航线,以及通往国内各大中城市的数百条航线。数条省内航线分别可通往大理、丽江、香格里拉、西双版纳、昭通、芒市、普洱、文山、保山、腾冲、临沧、泸沽湖等。
Kunming has air connections with several Chinese and Southeast Asian cities. Kunming is served by Kunming Changshui International Airport (KMG), which opened in June 2012, replacing the older international airport, which was located 4–5 km (2.5–3.1 mi) southeast of central Kunming.
【参考译文】昆明与中国和东南亚的多座城市有航空联系。昆明长水国际机场(KMG)为昆明提供航空服务,该机场于2012年6月启用,取代了位于昆明市中心东南4-5公里(2.5-3.1英里)的旧国际机场。
The now defunct Yunnan Airlines was headquartered in Kunming until it was acquired by China Eastern Airlines. China Southwest Airlines used to operate routes to and from Kunming, until it was merged with Air China.
【参考译文】现已不存在的云南航空公司曾以昆明为总部,后被中国东方航空收购。中国西南航空公司曾运营往返昆明的航线,后与国航合并。
Lucky Air is a budget airline based in Kunming and operates scheduled services from Dali to Kunming and Xishuangbanna, and plans to expand to other areas of China.
【参考译文】祥鹏航空是一家总部位于昆明的廉价航空公司,运营大理至昆明和西双版纳的定期航班,并计划扩展至中国的其他地区。
5.3 公路 | Highway
See also: Asian Highway Network and Eurasian Land Bridge【另见:亚洲公路网和欧亚大陆桥】
China National Highways 108, 213 and 320 intersect in Kunming. Highways link Kunming to Thailand, Vietnam and Laos, and provide Yunnan province access to seaports of Southeast Asia.
【参考译文】中国国道108线、213线和320线在昆明交汇。公路将昆明与泰国、越南和老挝连接起来,为云南省通往东南亚海港提供了通道。
昆明的公路系统由市区2环快速3环路及2013年底全线贯通的昆明绕城高速组成。此外还有108国道、213国道、245国道、248国道、320国道、324国道、京昆高速、杭瑞高速、沪昆高速、汕昆高速、广昆高速、银昆高速以及多条高速公路和省道构成。
5.4 城市公路交通 | Road and transit
Yunnan has built a comprehensive highway system with roads reaching almost all the major cities or towns in the region. Bus travel across the region is extensive. Buses head from Kunming to destinations such as Dali and Lijiang several times a day.
【参考译文】云南已经建立起一个覆盖全省各大城市或城镇的综合性公路系统。该地区的公交出行十分便捷。每天都有多趟从昆明开往大理、丽江等地的公交车。
昆明市区交通主要以公共汽车为主,公共汽车线路现已覆盖二环路内超过95%的地方,并且覆盖大多数二环以外的地方。线路数量超过200多条。昆明的公共汽车主要有两家巴士公司经营,即昆明公交公司和昆明城巴。城区拥有多条公交车道,如人民路,广福路,西福路等。
其中行驶在北京路公交车道上的由昆明公交和昆明城巴共同运营的236路车是昆明第一条快速公交线路,线路配备多辆铰接式公共汽车。其实这条线路不完全是快速公交,因为它不具备快速公交的一些特点。但是此条线路在上下班高峰时平均每40多秒就有一辆车出发。该线路由北市区公交车场发车从北到南,贯穿整个昆明城,到达昆明站站前广场,来回行驶。237线行驶在人民路公交车道上,此外还有A1线从昆明世博园到云南民族村。其他重要的公交线路还有5路,1路,26路,52路,71路,84路,127路,129路,107路,170路等。
There are four major long-distance bus stations in Kunming with the South Bus Station and Railway Square Bus Station being the most primary.
【参考译文】昆明有四个主要的长途汽车站,其中南部汽车站和火车站广场汽车站是最主要的两个。
- South Bus Station faces the Kunming Railway Station in Beijing Xi Lu, with standard, luxury, express and sleeper buses departing for all over Yunnan and neighboring provinces.
【参考译文】南部汽车站(South Bus Station)位于北京路西站对面,提供前往云南全省及邻近省份的标准、豪华、快车和卧铺客车服务。 - Railway Square Bus Station is smaller than SBS and the majority of the buses depart from the station are private-run. Usually no fixed schedules are available and buses will leave when they are full. There are standard and sleeper services to Dali, Jinghong and elsewhere in Yunnan.
【参考译文】火车站广场汽车站(Railway Square Bus Station)规模较小于南部汽车站,且大部分发出的班车为私营。通常没有固定的发车时间表,车辆满载后即发车。提供前往大理、景洪及云南其他地区的标准和卧铺服务。
Leaving China by road into Vietnam and Laos is also possible through the respective crossings at Hekou in southeastern Yunnan or Bian Mao Zhan in Xishuangbanna.
【参考译文】通过云南东南部的河口或西双版纳的勐腊磨憨口岸,还可以驾车出境进入越南和老挝。
The Kunming–Bangkok Expressway is the first expressway from China to Bangkok via Laos. The 1,800 km (1,100 mi) long Kunming–Bangkok Expressway begins at Kunming going down to Ban Houayxay in Laos; it then crosses the Mekong River to Chiangkhong in Thailand and eventually reaches Bangkok.
【参考译文】昆明-曼谷高速公路是第一条经老挝从中国通往曼谷的高速公路。全长1800公里(1100英里)的昆明-曼谷高速公路起点为昆明,经老挝会晒,跨过湄公河到达泰国的清孔,最终到达曼谷。
At the 14th Greater Mekong Subregion Ministerial Conference in July 2007, China, Laos and Thailand signed an agreement on the construction of a new bridge over the Mekong River to connect Chiangkhong in Thailand and Ban Houayxay in Laos, to the Kunming–Bangkok Highway. The completion of the new bridge over the Mekong River will help connect China’s southeast provinces with Bangkok. With capital investments from both China and Thailand, the bridge is expected to be completed in 2011 and will be the last link in the highway system that winds through the Mekong River region.
【参考译文】在2007年7月举行的第十四届大湄公河次区域部长级会议上,中国、老挝和泰国签署了一项协议,决定在湄公河上修建一座新桥,连接泰国的清孔和老挝的会晒,以接入昆明-曼谷高速公路。这座横跨湄公河的新桥一旦建成,将有助于连接中国的东南各省与曼谷。该桥由中泰两国投资,预计于2011年完工,将成为蜿蜒穿过湄公河流域的高速公路系统的最后一环。
5.4.1 本地交通 | Local transit
Public buses and taxis are the two main means of transport within the city. A metro system is currently under construction (see Kunming Metro).
【参考译文】公交车和出租车是昆明市内主要的两种交通工具。目前,地铁系统正在建设中(见昆明地铁)。
Nearly two hundred public bus lines crisscross the city center, covering the whole prefecture.
【参考译文】近200条公交线路在市中心纵横交错,覆盖整个市区。
Cycling is common, and many hotels around the Kunming Railway Station provide bicycle rental services.
【参考译文】骑行在昆明很常见,昆明火车站周边的许多酒店都提供自行车租赁服务。
Conscious of its growing traffic issues, the city is currently renovating a pedestrian-friendly city centre.
【参考译文】鉴于日益严重的交通问题,昆明目前正在对市中心进行改造,以打造更加友好的步行环境。
5.4.2 昆明市中心 | Central Kunming
The city hangs off two main thoroughfares: Beijing Lu forms the north–south axis, passing just east of the center as it runs for 5 km (3.1 mi) between the city’s two trains stations; while Dongfeng Lu crosses it halfway along, divided into east (Dongfeng Dong Lu), middle (Dongfeng Zhong Lu) and west (Dongfeng Xi Lu) sections as it cuts right through the business center. The far end runs out of the city as Renmin Xi Lu, the first leg of the Burma Road. Most of the city’s famous hotels and foreign consulates lies along Dongfeng Dong Lu and the southern half of Beijing Lu, while the majority of specific landmarks and shopping district are north and west of the center around Dongfeng Xi Lu and Cuihu Park (Green Lake Park). Circling most of this is the city’s first highway ring road, Huancheng Lu, though others are planned.
【参考译文】昆明市中心主要由两条主干道构成:北京路作为南北轴线,贯穿城市南北,全长5公里(3.1英里),位于市中心以东,连接着城市的两个火车站;东风路则在中途与其相交,并贯穿商业中心,分为东风东路、东风中路和东风西路三段。其远端延伸出城,成为滇缅公路的第一段——人民西路。昆明的大多数知名酒店和外国领事馆都位于东风东路和北京路南部,而大多数特定的地标和购物区则位于市中心以北和以西的东风西路和翠湖公园(绿湖公园)周边。环绕这些区域的是昆明的第一条高速公路环线——环城路,尽管未来还有其他环线规划。
6. 经济 | Economy
Kunming has three economic advantages over other cities in southwest China: significant natural resources, a large consumer market and a mild climate. Due to its position at the center of Yunnan, one of China’s largest producers of agricultural products, minerals and hydroelectricity, Kunming is the main commercial hub for most of the province’s resources.
【参考译文】昆明相比中国西南部的其他城市具有三大经济优势:丰富的自然资源、庞大的消费市场和温和的气候。由于它位于中国最大的农产品、矿产和水力发电生产省份之一的云南的中心,昆明是该省大部分资源的主要商业枢纽。
2022年,全市实现地区生产总值7541.37亿元,按可比价格计算,比上一年增长3%,两年平均增长3.3%。其中,第一产业增加值326.96亿元,增长4.4%;第二产业增加值2413.39亿元,增长3.2%;第三产业增加值4801.02亿元,增长2.7%。三次产业结构为4.3∶32∶63.7,三次产业对GDP增长的贡献率分别为7.2%、33.3%和59.5%,分别拉动GDP增长0.2个百分点、1个百分点和1.8个百分点。民营经济实现增加值3028.79亿元,比上一年增长3.4%,占GDP比重为40.2%。全年民营经济实现增加值3028.79亿元,比上年增长3.4%,占GDP比重为40.2%。全市新登记市场主体27.43万户,同比增加8.55万户,增长45.3%,其中企业新登记9.11万户,增长31.8%;个体工商户18.29万户,增长53.4%。市场主体总量达120.14万户,增长19.6%。全年居民消费价格比上年上涨1.7%。其中,食品烟酒类上涨1.6%,衣着类上涨0.6%,居住类上涨0.1%,生活用品及服务类上涨0.5%,交通和通信类上涨6.0%,教育文化和娱乐类上涨0.9%,医疗保健类上涨1.6%,其他用品和服务类上涨2.4%。全年商品零售价格比上年上涨2.7%。全年一般公共预算收入(同口径)614.57亿元,比上年下降13.6%。其中,税收收入503.46亿元,下降10.7%,占一般公共预算收入的比重81.9%。一般公共预算支出863.27亿元,下降7.0%。其中,民生支出634.91亿元,占全市一般公共预算支出的比重73.5%。全年城镇新增就业21.59万人,城镇下岗失业人员再就业4.13万人,年末城镇登记失业率为4.07%。农村劳动力转移就业11.71万人次[25]。
昆明正在努力建设成为中国面向西南开放的区域性国际城市。昆明区位独特,地处“9+2”泛珠三角区域经济合作圈、“1+1”中国-东盟自由贸易区经济圈和大湄公河次区域经济合作圈的交汇点。随着昆明至曼谷国际公路的通车,泛亚铁路的规划建设,以及正在建设中的昆明国际空港等重大基础设施的实施,昆明面向东南亚、南亚开放的“桥头堡”作用日益凸现。
改革开放以来,昆明经济始终保持快速健康发展的良好态势,综合经济实力进入西部地区先进行列。经过多年的发展,形成了卷烟、机电、生物资源、信息、商贸旅游等五大支柱产业。
In May 1995, the State Council approved Kunming as an Open City. By the end of 1995, the city had approved 929 overseas-funded enterprises with a total investment of $2.3 billion including $1.1 billion of foreign capital. More than 40 projects each had an investment of more than $9 million.
【参考译文】1995年5月,国务院批准昆明为对外开放城市。到1995年底,该市已批准929家海外投资企业,总投资额达23亿美元,其中外资11亿美元。有40多个项目的投资额超过900万美元。
农业持续、稳定、协调发展,结构调整成效明显,特色突出,“斗南花卉”、“呈贡蔬菜”成为国内外知名品牌。 工业形成了以机械、冶金、烟草加工等为主的体系,是云南省的工业基地和西南地区重要的工业城市。
Kunming’s chief industries are copper, lead and zinc production. Its iron and steel industry has been expanded. Salt and phosphate mines around Kunming are some of the largest in China. Yunnan Copper Company Limited, based in Kunming, is one of Yunnan’s largest mining corporations. From the late 1970s, Kunming’s main industries also came to include food and tobacco processing and the manufacture of construction equipment and machines. [citation needed]
【参考译文】昆明的主要产业是铜、铅和锌的生产。昆明的钢铁工业已经得到了扩展。昆明周边的盐和磷矿是中国最大的矿藏之一。总部位于昆明的云南铜业股份有限公司是云南省最大的矿业公司之一。从20世纪70年代末开始,昆明的主要工业还包括食品和烟草加工以及建筑设备和机械的制造。[需要引文]
Kunming is a center of engineering and the manufacture of machine tools, electrical machinery, equipment and automobiles (including heavy goods vehicles). It has a chemical industry, and plastics, cement works and textile factories. Its processing plants, which include tanneries, woodworking and papermaking factories, use local agricultural products. In 1997, Yunnan Tire Co. opened a tire plant in Kunming, with a capacity to produce two million tires per year. [citation needed]
【参考译文】昆明是工程和机床、电机、设备及汽车(包括重型货车)制造业的中心。它还拥有化工行业、塑料业、水泥厂和纺织厂。其加工厂,包括制革厂、木材加工厂和造纸厂,均使用当地农产品作为原料。1997年,云南轮胎厂在昆明开设了一家轮胎厂,年生产能力为200万条轮胎。[需要引文]
第三产业在国民经济中的比重日益增大,商贸、旅游、信息、现代服务业快速发展,对全市经济社会的发展起到了重要的带动作用和促进作用。 2008年昆明经济发展在全国发展势头迅猛,经济形势和效果得到了全国各界的肯定。2008年获得“全国十大浙商最佳投资城市”,与成都、大连、包头、广州一起荣获“2008中国制造业最佳投资城市”等称号。
南屏街是位于昆明市中心的商业街。其他商圈还有青年路、白塔路、北京路北段、昆明螺蛳湾国际商贸城、大观商业城、小西门等。
6.1 开发区 | Development zones
Kunming has two major development zones, Kunming High-tech Industrial Development Zone (biological medicine, new materials, electronic information, photoelectron, agriculture) and Kunming Economic and Technology Development Zone (mechanical equipment production, biological science and food industry, information industry, software).
【参考译文】昆明有两个主要开发区,即昆明高新技术产业开发区(涵盖生物医药、新材料、电子信息、光电子、农业等领域)和昆明经济技术开发区(涵盖机械设备制造、生物科学与食品工业、信息产业、软件等领域)。
6.2 工业园区 | Industrial parks
There are 30 key industrial parks promulgated and recognized by National Development and Reform Commission in Yunnan Province.[54]
【参考译文】云南省有30个由国家发展和改革委员会公布并认定的重点工业园区。[54]
The largest include:
【参考译文】其中最大的包括:
- Chenggong Industrial Park【呈贡工业园区】
- Anning Industrial Park【安宁工业园区】
- Songming Yanglin Industrial Development Zone【嵩明杨林工业开发区】
- Dongchuan Special Industrial Park【东川特色工业园区】
- Xundian Special Industrial Park【寻甸特色工业园区】
- Kunming Haikou Industrial Park【昆明海口工业园区】
6.3 企业 | Companies
As of 2008, Kunming is home to 65 of the Top 100 Enterprises in Yunnan Province. The top 100 enterprises were based on their revenues for 2007. Hongta Group, with revenues of some RMB39.88 billion for 2007 topped the list. The tobacco sector remains the largest sector in the province.
【参考译文】截至2008年,昆明拥有云南省百强企业中的65家。这些百强企业是根据它们2007年的收入进行排名的。红塔集团以2007年收入约398.8亿元人民币位居榜首。烟草行业仍然是该省最大的行业。
6.3+1 花卉产业 | Flower industry
Yunnan has developed into the largest flower export base in Asia, with many Dutch experts having transferred technology to the area. The Dounan Flower Market, located in suburban Kunming, is the largest in China with daily sales of 2.5 million yuan (US$300,000) from the 2 million sprays of flowers (as of 2006). The provincial government agency, the Yunnan Flower Association, regulates the industry.[55]
【参考译文】云南已经发展成为亚洲最大的花卉出口基地,许多荷兰专家已将技术转移到该地区。位于昆明郊区的斗南花卉市场是中国最大的花卉市场,每天销售200万枝花卉(截至2006年),销售额达250万元人民币(30万美元)。云南省政府机构——云南省花卉产业联合会负责监管该行业。[55]
6.5 物流 | Logistics
Kunming East Station is at present Yunnan province’s only container handling depot, with direct links to only three provinces; Guangdong, Guizhou and Sichuan. It also has direct access to the metropolitan district of Chongqing.
【参考译文】昆明东站目前是云南省唯一的集装箱处理场站,仅与广东、贵州和四川三个省份有直接联系。此外,它还可以直达重庆市主城区。
The Jiaying Depot is connected with the new system of highways built linking Yunnan to the increasingly important markets of Southeast Asia, facilitating cheap Chinese exports to the region and granting resource-poor China greater access to the region’s massive raw material resources. Yunnan has thereby become a progressively important area in the Southwest‘s rail logistics both in terms of national and international logistics.
【参考译文】嘉谊场站与新建的云南通往东南亚日益重要的市场的高速公路系统相连,促进了中国向该地区的廉价出口,并使资源匮乏的中国能够更大程度地获取该地区的丰富原材料资源。因此,云南在西南地区的铁路物流中,无论是国内还是国际物流,都逐渐成为一个重要的区域。
6.6 太阳能 | Solar energy
In July 2008, Kunming began to implement a program to transform the city’s solar energy industry into a US$8.8 billion industrial base in China by 2013. Kunming receives an annual average sunshine of more than 2,400 hours. Each 1 kW PV system has the potential to generate 1500 kilowatt-hours of electricity a year from solar energy. [citation needed]
【参考译文】2008年7月,昆明开始实施一项计划,旨在将该市的太阳能产业打造成一个到2013年规模达88亿美元的中国产业基地。昆明年均日照时间超过2400小时。每1千瓦的光伏系统每年有潜力从太阳能中发电1500千瓦时。[需要引文]
As of 2007, the Kunming Economic Committee listed about 130 solar energy enterprises in the city. Of these, 118 enterprises produce solar lamps and solar water heaters, with a combined total production value of about US$43.8 million, and 10 enterprises are engaged in solar photovoltaic cells manufacturing, with a total production value of about US$51.2 million.[56]
【参考译文】截至2007年,昆明市经济委员会列出了该市约130家太阳能企业。其中,118家企业生产太阳能灯具和太阳能热水器,总产值约为4380万美元,10家企业从事太阳能电池板制造,总产值约为5120万美元。[56]
Suntech Power announced in December 2008 that it was jointly constructing a solar energy project with Yunnan Provincial Power Investment and other investors. The 1MW first-phase of the Shilin 66MW on-grid solar power station began generating power on 28 December 2009. The initial phase of the 66MW project was originally scheduled to start production in first half of 2010 while the 20MW second phase and 36 MW third phase were under construction.
【参考译文】2008年12月,尚德电力宣布正与云南省电力投资有限公司和其他投资者共同建设一个太阳能项目。石林66兆瓦并网太阳能电站一期1兆瓦项目于2009年12月28日开始发电。该66兆瓦项目的初期阶段原定于2010年上半年投产,而20兆瓦的二期项目和36兆瓦的三期项目正在建设中。
7. 社会与文化 | Society and culture
7.1 休闲和娱乐 | Leisure and entertainment
Within Kunming, the entertainment district has its focus around Kundu Square, with many cinemas, bars, clubs and restaurants. Food aside, one feature of less formal Yunnanese restaurants is that they often have a communal bamboo water pipe and tobacco for their customers. [citation needed] There are plenty of student bars and clubs. The city has several operatic troupes and indigenous entertainments which include huadeng, a lantern dance. Although indoor performances are lacking, there are often informal shows at the weekend outside the Workers’ Cultural Hall and in Cuihu Park. There are similar shows at the Yunnan Arts Theater on Dongfeng Xi Lu. Kunming’s main cinema house is on the south side of the Dongfeng Lu/Zhengyi Lu intersection. The other main multiplex, the XJS, at the junction of Wenlin Jie and Dongfeng Xi Lu.
【参考译文】在昆明,娱乐区主要集中在昆都广场附近,那里有许多电影院、酒吧、俱乐部和餐馆。除了美食之外,云南非正式餐馆的一个特色是它们经常为顾客提供共用的竹制水烟筒和烟草。[需要引文]这里有很多学生酒吧和俱乐部。该市有几个歌剧团和本土娱乐活动,包括花灯,一种灯笼舞。虽然室内表演不多,但通常在周末,工人文化宫外和翠湖公园内会有非正式的表演。在东风西路上的云南艺术学院剧院也有类似的表演。昆明的主要电影院位于东风路/正义路交叉口南侧。另一家主要的多厅式影院XJS位于文林街与东风西路交汇处。
7.2 语言 | Language
Further information: Kunming dialect【更多信息参见:昆明方言】
The Kunming dialect is very similar to that of Sichuan and Guizhou but uses the third tone much less than standard Chinese. Many terms are used only in Kunming dialect, such as “板扎” meaning ‘terrific’.
【参考译文】昆明方言与四川、贵州的方言非常相似,但与标准普通话相比,第三声的发音要少得多。许多词汇仅在昆明方言中使用,例如“板扎”意为“棒极了”。
The pronunciations of certain Chinese characters are very different from Mandarin Chinese. For example, “鱼 (fish)” would be pronounced as “yi” in Kunming dialect instead of “yu” in Mandarin Chinese; “街 (street)” would be pronounced as “gai” instead of “jie”.
【参考译文】一些汉字的发音与普通话有很大的不同。例如,“鱼(鱼)”在昆明方言中读作“yi”,而在普通话中读作“yu”;“街(街道)”在昆明方言中读作“gai”,而在普通话中读作“jie”。
When someone speaks Mandarin Chinese with a strong Kunming accent, it’ll be called Mapu (马普), short for Majie (马街, a place in Kunming) Mandarin Chinese.
【参考译文】当有人用浓重的昆明口音说普通话时,这被称为“马普”,是“马街普通话”的简称,马街是昆明的一个地方。
The Kunming Dialect is slowly dying due to it being ‘informal’ and is being replaced by Mandarin Chinese. Nevertheless, it is still spoken by a decent number of residents today. Sometimes this is called dirt language or slum language (土话)
【参考译文】由于昆明方言被视为“非正式”语言,正在逐渐被普通话取代,因此昆明方言正慢慢消亡。然而,如今仍有相当数量的居民使用这种方言。有时这被称为“土话”或“贫民区语言”。
7.3 旅游 | Tourism
Kunming attracts domestic and foreign tourists year-round. At the center of Yunnan and as its capital, Kunming is also a transport hub for tourists heading to other parts of Yunnan such as Dali, Lijiang and Shangrila.
【参考译文】昆明全年吸引着国内外游客。作为云南省的中心和省会,昆明也是游客前往云南其他地区如大理、丽江和香格里拉的重要交通枢纽。
昆明还是自然景观和人文景观的荟萃之地。悠久的历史、独特的地质结构,为昆明留下了众多的文物古迹和风景名胜。昆明市是一个发展中的国际旅游城市,因此昆明是集自然风光和民族风情为一体的多功能的四季皆宜的旅游胜地。
7.3.1 市内景点
在昆明传统的城市中轴线——三市街、正义路上,有金马碧鸡坊、近日公园。金马碧鸡坊南面不远,高大的东西寺塔为南诏国遗物,是昆明最古老的建筑物之一。位于昆明市中心西北侧的翠湖占地面积352亩,环湖植柳,湖中多荷花,目前是一座免费开放的市民公园。1985年以来,每年冬天的12月到来年的3月,有成千上万只北方飞来的红嘴鸥在翠湖越冬,“翠湖观鸥”成为昆明热门的特色景观之一。周边聚集了一批五星级酒店、酒吧、茶馆、西餐馆。不远处有圆通山动物园。到了市中心,建设路有条小巷子,名叫文化巷。是年轻人的聚集地。
滇池周边有不少名胜古迹,其中大观楼以清朝名士孙髯翁长达180字的对联著称。之前滇池湖水受到蓝藻污染的问题近年来有了大幅度的缓解,可亲临湖畔或从西山森林公园远眺滇池风光。
昆明市区东北部的金殿是一座仿造武当山太和宫铜殿建造的金碧辉煌的明代建筑,园内拥有众多品种的茶花。毗邻的昆明世界园艺博览园是1999年昆明世界园艺博览会的主会址,占地达220公顷,植被覆盖良好。昆明市内及市郊拥有不少佛教寺庙,例如筇竹寺、圆通寺、昙华寺、西山华亭寺等;还有一些近代遗迹,如云南陆军讲武堂与西南联合大学旧址。此外还有黑龙潭、云南民族村等公园。
Conference and exhibition venues in Kunming include the Kunming International Convention and Exhibition Center and the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Hall.
【参考译文】昆明的会议和展览场所有昆明国际会展中心和云南省科技馆。
7.3.2 全国重点文物保护单位
- 太和宫金殿
- 地藏寺经幢
- 云南陆军讲武堂 (旧址)
- 聂耳墓
- 妙湛寺金刚塔
- 石寨山古墓群
- 筇竹寺
- 惠光寺塔和常乐寺塔
- 曹溪寺
- 安宁文庙
- 真庆观古建筑群
- 王仁求碑
- 马哈只墓碑
- 石龙坝水电站
- 国立西南联合大学(旧址)
- 抗战胜利纪念堂
- 大观楼
- 福林堂
- 丹桂村中央红军总部驻地旧址与金沙江皎平渡口
7.3.3 周边景点
Kingdom of the Little People, a theme park featuring performers with dwarfism, is also located near Kunming.[51]
【参考译文】以侏儒演员为特色的主题公园“小人国”也位于昆明附近。[51]
7.4 体育运动 | Sports
Every year, many Chinese and international athletes come to Kunming for high-altitude training. The city has been China’s national high-elevation training base for more than 30 years. There are two major training complexes, Hongta Sports Center and Haigeng National Training Center.[52]
【参考译文】每年,许多中国和国际运动员都会来到昆明进行高原训练。昆明作为中国国家级高原训练基地已有30多年的历史。这里有两个主要的训练综合体:红塔体育中心和海埂国家训练中心。[52]
Hongta Sports Center was built in 2000 by Hongta (Red Pagoda) cigarette company, at a cost of US$58 million. Located near Haigeng Park, the complex is mostly used by professional athletes, but also acts as a sports club for the general public. Every weekend, it hosts amateur football matches. Aside from about 10 football pitches, including one surrounded by a running track, Hongta also has a 50-metre (160-foot) swimming pool, a badminton gymnasium, tennis courts and a basketball court. It also has one of China’s few ice hockey rinks, and a workout room with treadmills and weightlifting machines. There are also game rooms for air hockey; also pool tables and a basement bowling alley. The complex comes complete with a 101-room hotel and restaurant.[52]
【参考译文】红塔体育中心由红塔(红塔山)烟草公司于2000年斥资5800万美元建造。该综合体位于海埂公园附近,主要供专业运动员使用,但同时也对公众开放,作为体育俱乐部。每个周末,这里都会举办业余足球比赛。除了大约10个足球场(其中一个被跑道环绕)外,红塔体育中心还设有50米(160英尺)的游泳池、羽毛球馆、网球场和篮球场。这里还拥有中国少数几个冰球场之一,以及配备跑步机和举重机的健身房。此外,还有空气曲棍球游戏室、台球桌和地下保龄球馆。该综合体还配备有一家拥有101间客房的酒店和餐厅。[52]
Haigeng National Training Center is located ten minutes away from Hongta on Dianchi (Lake Dian) near Kunming’s award-winning Lakeview Golf Club and new condominium developments. This complex dates from the late 1970s and was built by the government specifically to specialize in high-altitude training.[52]
【参考译文】海埂国家训练中心位于红塔体育中心以东约十分钟车程的滇池(滇池湖)畔,靠近昆明获奖颇多的湖景高尔夫俱乐部和新的公寓开发区。这个训练中心建于20世纪70年代末,是政府专门为了高原训练而建造的。[52]
7.4.1 高尔夫球 | Golf
Golf is a major attraction in Kunming. There are four golf courses within an hour’s drive of downtown. For the last six years [when?], Spring City Golf and Lake Resort in nearby Yiliang County has reigned as the best golf course in China and Hong Kong according to US Golf Digest. In 2004, it was named Asia’s best golf resort by Asian Golf Monthly.[53] It hosts the Kunming Leg of the Omega China Tour.
【参考译文】高尔夫是昆明的一大亮点。在市中心一小时车程范围内有四座高尔夫球场。据《美国高尔夫文摘》报道,在过去六年[何时?]里,附近宜良县的春城高尔夫湖畔度假村一直被评为中国和香港地区最佳高尔夫球场。2004年,该度假村被《亚洲高尔夫月刊》评为亚洲最佳高尔夫度假村。[53]这里还举办了欧米茄中国巡回赛昆明站比赛。
Kunming has attracted foreign investment in golf course development. “Spring City” Golf Resort is a US$600 million project that began as an investment led by Singapore’s Keppel Land Group in 1992. Jack Nicklaus and course designer Robert Trent Jones, Jr designed the two courses.[53]
【参考译文】昆明吸引了外国对高尔夫球场开发的投资。“春城”高尔夫度假村是一个耗资6亿美元的项目,该项目始于1992年,最初是由新加坡吉宝置地集团主导的一项投资。杰克·尼克劳斯和球场设计师小罗伯特·特伦特·琼斯设计了这两座球场。[53]
7.4.2 体育设施 | Sport facilities
Major sports facilities include:
【参考译文】主要体育设施包括:
- Tuodong Sports Center, a multi-purpose venue
【参考译文】拓东体育中心,一个多功能场馆 - Golf: Spring City Golf and Lake Resort, its ‘Mountain Course’ was designed by Jack Nicklaus
【参考译文】高尔夫:春城高尔夫湖畔度假村,其“山地球场”由杰克·尼克劳斯设计 - Lakeview Golf Villa
【参考译文】湖景高尔夫别墅 - Cuihu Park tennis courts
【参考译文】翠湖公园网球场 - Kunming Municipal Athletic Center
【参考译文】昆明市体育中心 - Kunming Gymnasium
【参考译文】昆明市体育馆 - Yunnan Provincial Stadium, home to Hongta Yunnan Football Club
【参考译文】云南省体育场,红塔云南足球俱乐部的主场 - Wuhua District Stadium
【参考译文】五华区体育场
7.5 教育和研究 | Education and research
Kunming remains a major educational and cultural center in the southwest region of China, with universities, medical and teacher-training colleges, technical schools, and scientific research institutes. As of 2024, it was listed among the top 100 cities in the world by scientific research output.[8]
【参考译文】昆明仍然是中国西南地区重要的教育和文化中心,拥有大学、医学院、师范学院、技术学校和科学研究所。截至2024年,昆明在科学研究成果方面位列世界前100名城市之列。[8]
7.5.1 高等院校 | Colleges and universities
See also: List of universities and colleges in Yunnan【另请参阅:云南省高等院校名单】
- 公办本科(12所)
- 民办本科
- 独立学院
- 军事院校
- 中国人民解放军陆军边海防学院昆明校区
7.5.1.1 云南大学 | Yunnan University
Yunnan University (云南大学), located in Kunming, is one of the largest and the most prestigious universities in China and is the only university in Yunnan province which has been developed into a “National Key University”. It was founded in 1922, as “University of the Eastern Land”. Its name has been changed six times subsequently. The institution has 17 schools on the local campus and 3 independent schools located in other cities. It claims the largest and best law school in Yunnan province.
【参考译文】位于昆明的云南大学(Yunnan University)是中国规模最大、声望最高的大学之一,也是云南省唯一一所被发展为“国家重点大学”的高校。它创办于1922年,当时名为“东陆大学”。之后,它的名字又经历了五次更改。该校在本部设有17个学院,并在其他城市设有3所独立学院。云南大学声称拥有云南省规模最大、最好的法学院。
7.5.1.2 云南师范大学 | Yunnan Normal University
Yunnan Normal University (云南师范大学) was founded in 1938 as the National Normal College of Southwestern Union University. In 1946, when some faculties returned to the north of China, it changed its name to National Kunming Normal College. It now as 6 campuses in Kunming itself and other cities. With 22 schools, it has an enrollment of some 33000 undergraduate students.
【参考译文】云南师范大学(Yunnan Normal University)创办于1938年,初名国立西南联合大学师范学院。1946年,部分院系北迁后,其更名为国立昆明师范学院。如今,该校在昆明及其他城市拥有6个校区。学校下设22个学院,约有33000名本科生在读。
7.5.1.3 昆明理工大学 | Kunming University of Science and Technology
Kunming University of Science and Technology (昆明理工大学) was established in 1954 and was given “key university” status in 2010. In 2017, it had 3 campuses in Kunming housing 24 schools and had an enrollment of 27000 undergraduates.
【参考译文】昆明理工大学(Kunming University of Science and Technology)创建于1954年,并于2010年被授予“重点大学”地位。2017年,该校在昆明拥有3个校区,下设24个学院,约有27000名本科生在读。
7.5.1.4 云南民族大学 | Yunnan Nationalities University
Yunnan Nationalities University was founded in 1951 as Yunnan Nationalities College. It is now one of six “key” universities in the province. It has established cooperative relations with 26 foreign universities including University of Bergen in Norway, La Trobe University in Australia, and University of Virginia in the United States. The university has a Nationalities Museum, which contains more than 20000 rare exhibits. There are more than 23000 undergraduates on campus.
【参考译文】云南民族大学始创于1951年,时称云南民族学院。如今,它是该省六所“重点”大学之一。该校已与包括挪威卑尔根大学、澳大利亚拉筹伯大学和美国弗吉尼亚大学在内的26所外国大学建立了合作关系。云南民族大学设有一座民族博物馆,馆内收藏有超过20000件珍稀展品。目前,该校有23000多名本科生在读。
7.5.1.5 华洋书院 | Huayang Academy
Huayang Academy is a specialist Chinese language training centre considered unique for offering training Kunming dialect as well as standard Mandarin. Its locality is a popular centre of Western culture in Kunming, attracting numerous foreign-owned businesses.[63]
【参考译文】华洋书院是一家专门的语言培训中心,因其提供昆明方言和标准普通话的培训而被认为独具特色。它位于昆明的一个受欢迎的西方文化中心,吸引了众多外资企业。[63]
7.5.2 管理培训 | Management training
The Shanghai-based China Europe International Business School, aka CEIBS, will launch in 2009 its Business Development Certificate Programme in Kunming. With the Business Development Certificate Programme, CEIBS and program partner Frankfurt School of Finance & Management aim to train approximately 500 Chinese managers in the coming four years, with the first phase of the program beginning in 2008 in Hefei, the capital of Anhui province. Kunming and Harbin will be the focus of the program’s expansion in 2009. The program is part of a two million Euro umbrella project funded by the EU, which also includes another program that provides scholarships for MBA students from China’s less-developed regions.[64]
【参考译文】总部位于上海的中欧国际工商学院(CEIBS)将于2009年在昆明推出其商务发展证书课程。通过这一课程,中欧国际工商学院及其课程合作伙伴法兰克福金融管理学院计划在未来四年内培训约500名中国管理人员。该课程的第一阶段已于2008年在安徽省省会合肥启动。2009年,该课程将重点扩展至昆明和哈尔滨。该课程是欧盟资助的一项200万欧元综合性项目的一部分,该项目还包括为来自中国欠发达地区的MBA学生提供奖学金的另一项课程。[64]
7.5.3 研究机构 | Research institutes
- Solar Energy Research Institute of Yunnan Normal University
【参考译文】云南师范大学太阳能研究所 - Kunming Municipal Planning and Design Research Institute
【参考译文】昆明市规划设计研究院
中国科学院 | Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Kunming Branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) was established in 1957. It was formerly known as Kunming Office of CAS and was promoted and renamed into a branch in 1958. In 1962, Yunnan Branch combined with Sichuan Branch and Guizhou Branch to establish Southwest China Branch of CAS in Chengdu. In October 1978, Kunming Branch was reestablished at the approval of the State Council.
【参考译文】中国科学院昆明分院成立于1957年,前身为中国科学院昆明办事处,1958年升格并更名为分院。1962年,云南分院与四川分院、贵州分院合并,在成都成立中国科学院西南分院。1978年10月,经国务院批准,昆明分院重新建立。
As a working department of CAS, Kunming Branch now administers five research institutes:
【参考译文】作为中国科学院的工作部门,昆明分院目前管理以下五个研究所:
- Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
【参考译文】中国科学院昆明植物研究所 - Kunming Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
【参考译文】中国科学院昆明动物研究所 - Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
【参考译文】中国科学院昆明医学生物学研究所 - Kunming Primate Research Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences
【参考译文】中国科学院昆明灵长类研究中心 - Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Gardens in Menglun, Mengla County, Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, far southern Yunnan.
【参考译文】位于云南省最南端的西双版纳傣族自治州勐腊县勐仑镇的中国科学院西双版纳热带植物园。
At present, it has a total staff of 1,160, of whom 808 are professional researchers, seven are academicians and 343 are senior researchers. There are also 447 PhD degree students and 530 master’s degree students. The retired staff is 1,090. The Branch has set up three national key open labs, two CAS key open labs, five key labs set up by CAS and local province, three engineering centers, five doctoral sites, five post doctoral stations and national famous plant herbariums and halls of wildlife specimens and has a series of up-to-date research instruments and apparatus, computer networks and biodiversity information systems. The Branch has become an advanced comprehensive science research base in astronomy, geology and biology.
【参考译文】目前,昆明分院共有职工1160人,其中专业研究人员808人,院士7人,高级研究人员343人。此外,还有447名博士研究生和530名硕士研究生。退休人员1090人。分院建立了三个国家重点实验室、两个中国科学院重点实验室、五个中国科学院与地方共建重点实验室、三个工程中心、五个博士点、五个博士后流动站以及国家著名的植物标本馆和野生动物标本馆,并拥有一系列现代化的研究仪器和设备、计算机网络和生物多样性信息系统。昆明分院已成为天文学、地质学和生物学领域先进的综合性科学研究基地。
7.5.4 图书馆 | Libraries
- Yunnan Provincial Library【云南省图书馆】
7.6 特产
8. 外部交往
8.1 总领事馆
主条目:昆明领事机构列表
自1910年法国在昆明正式设立法国外交部驻云南府交涉员公署开始,意大利、英国、德国、美国和日本均曾经在昆明开设领事机构,均于1949年前关闭。[26]
中华人民共和国成立后,1955年5月30日,越南民主共和国在昆明开设领事馆,同年8月26日,缅甸也在昆明设立了总领事馆,因其国内财政问题于1963年闭馆,随着中越关系的恶化,越南驻昆明总领事馆也于1978年被勒令关闭,自老挝于1993年4月25日设立总领事馆以来,昆明现实际有外国领事机构7个。
The following countries have a diplomatic mission in Kunming:
【参考译文】以下国家在昆明设有外交机构:
- Consulates:[76]
【参考译文】领事馆:[76]- Bangladesh【孟加拉国】
- Cambodia【柬埔寨】
- Myanmar (Burma)[77]【缅甸】
- Laos【老挝】
- Malaysia[78]【马来西亚】
- Thailand【泰国】
- Vietnam【越南】
- Trade offices:
【参考译文】贸易办事处:- Australia【澳大利亚】
- Netherlands【荷兰】
8.2 友好城市
截至2023年,昆明市与28个城市结为国际友好城市:[27][28]
| 城市 | 国家 | 结好时间 |
|---|---|---|
| 藤泽市 | 1981年11月5日 | |
| 苏黎世 | 1982年2月17日 | |
| 舍夫沙万 | 1985年5月14日 | |
| 丹佛 | 1986年5月15日 | |
| 沃加沃加 | 1988年8月14日 | |
| 科恰班巴 | 1997年9月25日 | |
| 清迈 | 1999年6月7日 | |
| 曼德勒 | 2001年5月10日 | |
| 新普利茅斯 | 2003年8月11日 | |
| 吉大港 | 2005年8月18日 | |
| 于韦斯屈莱 | 2008年9月18日 | |
| 仰光 | 2008年12月1日 | |
| 金边 | 2011年6月8日 | |
| 波隆纳鲁瓦 | 2011年7月27日 | |
| 万象 | 2011年10月17日 | |
| 日惹市 | 2013年2月28日批准[注 3] | |
| 安塔利亚 | 2013年5月10日 | |
| 博克拉 | 2013年7月8日 | |
| 加尔各答 | 2013年10月23日 | |
| 斯克内克塔迪 | 2014年3月25日 | |
| 古晋南市 | 2014年8月25日批准 | |
| 岘港 | 2015年2月6日 | |
| 格拉斯 | 2016年3月27日 | |
| 奥洛穆茨 | 2017年8月17日 | |
| 高山市 | 2018年12月21日 | |
| 迪岑巴赫 | 2019年11月14日 | |
| 加济布尔 | 2020年10月12日批准 | |
| 布哈拉 | 2022年9月13日 |
9. 知名人物 | Notable residents
Notable people from Kunming include:
【参考译文】来自昆明的知名人士包括:
- Benedict Anderson, scholar (born in Kunming)
【参考译文】本尼迪克特·安德森,学者(出生于昆明) - Cai Xitao, botanist
【参考译文】蔡希陶,植物学家 - Chih-Kung Jen, physicist
【参考译文】詹志康,物理学家 - Wang Xiji, aerospace engineer and recipient of the “Two Bombs, One Satellite” Meritorious Award
【参考译文】王希季,航天工程师,荣获“两弹一星”功勋奖章 - Pierre Jean Marie Delavay, 19th-century French missionary, lived and died in Kunming
【参考译文】皮埃尔·让·马里·德拉韦,19世纪法国传教士,在昆明生活并去世 - Lamu Gatusa, professor and writer
【参考译文】拉木·加图萨,教授及作家 - He Yunchang, Chinese performance artist born in Kunming whose early, seminal works were also performed there[79]
【参考译文】何云昌,出生于昆明的中国行为艺术家,其早期开创性作品也在昆明上演[79] - Li Weiwei, Olympics handball player
【参考译文】李薇薇,奥运会手球运动员 - Liu Fang, pipa player
【参考译文】刘芳,琵琶演奏家 - Maran Brang Seng, Burmese politician (died in Kunming)
【参考译文】马拉兰·班朗森,缅甸政治家(在昆明去世) - Ma Yashu, actress
【参考译文】马雅舒,女演员 - Nie Er, composer (born in Kunming)
【参考译文】聂耳,作曲家(出生于昆明) - Frank Shu, Chinese-American astrophysicist, born in Kunming
【参考译文】弗兰克·舒,华裔美国天体物理学家,出生于昆明 - Xing Ruan, Chinese-Australian author and architect, born in Kunming
【参考译文】邢栾,出生于昆明的中澳作家和建筑师 - Song Wencong, aerospace engineer and aircraft designer
【参考译文】宋文骢,航天工程师和飞机设计师 - Tang Jiyao, general and warlord of Yunnan, died in Kunming
【参考译文】唐继尧,云南军阀及将领,在昆明去世 - Tong Yao, actress
【参考译文】童瑶,女演员 - Tu Wei-ming, ethicist (born in Kunming)
【参考译文】杜维明,伦理学家(出生于昆明) - Wang Hongni, triathlete and Asian Games gold medallist
【参考译文】王洪妮,铁人三项运动员,亚运会金牌得主 - Wen Yiduo, poet and scholar, (lived and assassinated in Kunming)
【参考译文】闻一多,诗人及学者(在昆明生活并被暗杀) - Anthony Zee, physicist
【参考译文】安东尼·齐,物理学家 - Zhang Xiaogang, artist, born in Kunming
【参考译文】张晓刚,艺术家,出生于昆明 - Zheng He, Ming dynasty explorer
【参考译文】郑和,明朝探险家 - Zhu De, military leader (studied in Kunming)
【参考译文】朱德,军事领袖(曾在昆明学习) - Zhu Youlang (Ming dynasty emperor), (fought and was executed in Kunming)
【参考译文】朱由榔(明朝皇帝),(在昆明作战并被处决)
Diplomats:
【参考译文】外交官:
- Auguste François, French consul in south China
【参考译文】奥古斯特·弗朗索瓦,法国驻华南领事 - George Soulié de Morant, French diplomat
【参考译文】乔治·苏里耶·德·莫朗,法国外交官 - John S. Service, American diplomat served in Kunming for two years
【参考译文】约翰·S·塞维斯,美国外交官,曾在昆明任职两年
National Southwestern Associated University:
【参考译文】国立西南联合大学:
- Chen Ning Yang, physicist
【参考译文】陈宁杨,物理学家 - Chen Yinke, linguist
【参考译文】陈寅恪,语言学家 - Feng Youlan, philosopher
【参考译文】冯友兰,哲学家 - Shiing-Shen Chern, mathematician
【参考译文】陈省身,数学家 - Ta-You Wu, physicist
【参考译文】吴大猷,物理学家 - Tsung-Dao Lee, physicist
【参考译文】李政道,物理学家 - Wang Yuan, mathematician
【参考译文】王元,数学家 - Wu Ningkun, professor emeritus
【参考译文】吴宁坤,荣誉退休教授 - Zhang Boling, founder of Nankai University
【参考译文】张伯苓,南开大学创始人

分享到: